Economic Concentration – Central California Winemaking Industry
The production and consumption of wine in the United States has evolved from a small scale to a national level. Beer and whiskey were the initial alcoholic drinks produced in the USA. Wine production was considered a niche activity, a perspective that led to the consideration of the beverage as an elite drink. It was difficult to purchase wine, which was mainly imported, while beer and whiskey were readily available (Silverman, Castaldi, & Baack, n.d). This led to reduced consumption in the USA. Today, wine is consumed nationally as a beverage that accompanies various meals. The USA is considered an open market that has low entry barriers. Despite the presence of imported wines, California’s wines dominate the market. The production of wine in Central California has been successful due to the favorable climate as well as the marketing and branding activities that wineries carry out.
Competition from imported wines has challenged the earlier market players. States such as New York and Washington have been producing wine, increasing the competition in this market, as shown in Table 1. However, the production of wine by numerous wineries is not enough to affect the price. Various factors affect the retail price of wine. These include the age of the wine, grape varieties, region of production, and ratings that are accorded. However, California wineries, which are well-known in the country, have improved the quality of their wines to match the consumers’ willingness to pay more due to this element (Swartz & Hira, 2014). In addition, this improvement has enabled the producers to offer a wide variety of wines at different price points to distributors, thus waiving off the competition. Therefore, competition led to the production of more wines with better quality.
Table 1: Wine production by states in 2011
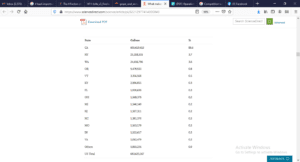
Source: (Swartz & Hira, 2014)
The organization of the supply chain in the wine industry is highly dependent on quality. Various approaches are employed in the industry, which range from oral agreements and formally binding contracts to management and common ownership of different aspects within the supply chain. These vertical decisions used to coordinate the supply chain are characteristic of California wineries (Franken, 2014). This choice of supply chain organization is necessitated by various factors, including the perishability of grapes. Thus, the growers and wine producers must be in close contact during harvest times. In addition, the quality of the grape affects the reputation of the winery, making this a critical element in the supply chain decisions.
Considering other players in the supply chain, the supply chain is subject to changes to achieve efficiency. Thus, California wine producers have altered the supply chain to offer distributors more varieties of wine and friendly prices (Franken, 2014). In addition, the change has also been necessitated by the demand from other countries requiring the wineries to export their products. These changes ensure that the final products reach the end consumer without unnecessary delays and further modifications. In other cases, the wineries use clubs to distribute their products directly to consumers who have signed up. Offering this option is important and acts as a reward for customer loyalty.
In the wine industry, the most important factors of production include climate and weather, growing practices, winemaking processes, and temperature. Central California’s climatic conditions favor the growth and fast maturity of grapes. The hotter climates lead to sweet wines due to the high sugar content of grapes, while cooler climates produce acidic wines that have lower sugar content. The production process is critical as it determines the type, color, sugar content, alcoholic content, character, body, and age of the wine (Swartz & Hira, 2014). This process begins by choosing high-quality grapes while they are still immature for harvesting. Judging by the superior quality of wines produced by California’s growers and wineries, the location’s climate, weather, and temperature are ideal for the crop. The other factors of production that carry less weight include human resources and land. While these factors are important for production, they rarely affect the quality of wine. The growers’ numbers do not matter as much as their experience in farming grapes for wine production.
As more wineries merge and acquire smaller ones to achieve economies of scale, the Central California producers are bound to face more challenges. Smaller wineries in other states are improving their marketing through customer relationships (Goodhue, Green, & Heien, 2008). Thus, producers have to innovate to promote their products to potential importers. Increasing its exports is a sustainable business approach that will act as a step towards reducing the trade deficits, as shown in Table 2 below.
Table 2: Balance of trade
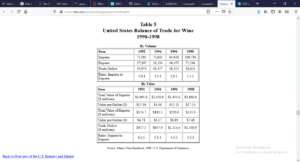
Source: (Silverman, Castaldi, & Baack, n.d)
References
Franken, J. R. (2014). Coordination of the California Wine-Grape Supply Chain.
Goodhue, R. E., Green, R. D., & Heien, D. M. (2008). Current Economic Trends in the California Wine Industry. Retrieved from https://s.giannini.ucop.edu/uploads/giannini_public/1e/e7/1ee7a361-2fac-4b5a-bf85-15c29b76ba7f/v11n4_2.pdf
Silverman, M., Castaldi, R., & Baack, S. (n.d). Competition in the Global Wine Industry: A U.S. Perspective. Retrieved from http://online.sfsu.edu/castaldi/bie/globcase.htm
Swartz, T., & Hira, A. (2014). What makes Napa Napa? The roots of success in the wine industry. Wine Economics and Policy, 3(1), 37-53.
ORDER A PLAGIARISM-FREE PAPER HERE
We’ll write everything from scratch
Question 

Central California Winemaking Industry
Select 1 of the economic concentrations (clusters) below:
Seattle-Tacoma-Olympia, WA aerospace/defense industry
Central California winemaking industry
Hollywood movie industry
Silicon Valley Technology hub
Texas / Louisiana Gulf Coast crude oil and natural gas production and refining
Pre-1994 vs. Post-1994 US auto and light truck production and the reasons for the change in economic concentration
Write a 700- to 1,050-word paper evaluating economists’ assessments of the role the 4 factors of production played in determining how the economic concentration you selected has evolved. Complete the following in your paper:
Analyze how the economic concentration in the area you chose was influenced by competition and pricing.
Analyze how the economic concentration in the area you chose influenced the supply chain.
Analyze which of the 4 factors of production were the most and least important in determining the economic concentration of the area you chose.
Predict changes you anticipate for the area of economic concentration you chose. Support your predictions.
Consider the resources provided and other academically appropriate sources. The use of charts and tables to illustrate data is highly encouraged.
Cite at least 2 academically credible sources.
