Discussion – The Monetary System
The Dollar and Value and Requirements for Something to Be Considered Money
Money has taken different forms through the ages, including shells, beads, wheels, and animals like cows. Whatever form that money has assumed in the past or present must possess certain elements. First, money stores value. If I earn $1 to say and keep it, its value remains the same tomorrow. The positive aspect of money’s ability to hold value is that it does not rot, unlike other perishable elements or mortal living things.
Secondly, money is a medium of exchange. This means that people can use money for transactions. If one walks into a supermarket, they can obtain certain goods in exchange for a certain amount of money. Thirdly, money has liquidity, which is the ease of transforming it into different elements such as an asset and vice versa. Finally, money is a unit of account because it provides a clear measure for every good or service. Also, the dollar’s value is essential because it legalizes it as a unit of account that is likely to be accepted by other people (Mankiw, 2021). Without its value, it would be challenging to consider it as money because its ability to function as a medium of exchange would be limited.
The Money Supply and the Respective Amounts in the Total Money Supply for the United States
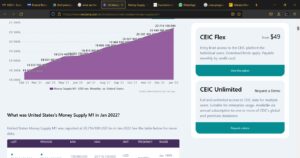
The Fed manages the money supply in the US. Money supply refers to the amount of money circulating in the economy. Additionally, the supply considers notes, coins, as well bank reserves. To increase the money supply, the Fed lowers the interest rates, which leads to greater and more investments. In January 2022, reports revealed that the country’s money supply as a medium of exchange (M1) was USD$20,716.100 billion. This amount has been rising steadily through the years.
Note: United States Money Supply M1. CEIC Data. (2021).
The Primary Functions of the Fed and the Role of the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) In the Economy
The Fed is responsible for two primary roles. First, it regulates banks to ensure that the banking system is healthy. Notably, the Fed monitors the financial status of each bank and clears checks to facilitate transactions. It also provides loans to banks when banks require credit. Secondly, the Fed controls the money supply through the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC). The FOMC meets every six weeks to discuss the economy’s condition while considering potential changes in monetary policies. FOMC empowers the Fed to either increase or decrease the dollars within the country’s economy (Mankiw, 2021).
The Role of Financial Institutions (Commercial Banks and Other Institutions)
Commercial banks and other institutions serve as a depository. When people have currency, they deposit it in the banks and access it later. In addition, banks provide credit in the form of loans. According to the Fed’s regulations, a percentage of the depository is provided for loans, while the rest is retained in the reserves.
Fractional-reserve Banking
Fractional reserve banking is a system that allows banks to hold partial amounts of the deposits in reserve. Government regulations determine the fraction of reserves that can be used for credit. The system creates liabilities for consumers who access the money for various reasons and pay it back with interest.
Available Tools to the FED for Controlling the Money Supply
The Fed influences money supply through open market operations, lending to banks, setting reserve requirements, and paying interest on reserves. The Fed uses open market operations most frequently because they are easy to use (Mankiw, 2021). As the easiest method, open market operations may be the most effective because the Fed can use them at any time to achieve the desired goal.
How the Money Multiplier Helps To Determine Monetary Policy Effects
The multiplier effect occurs when the banks generate more money using the reserves. The money is made through deposits and bank loans (Mankiw, 2021). Therefore, when monetary policies increase the fraction of reserves, it reduces the money that a bank makes through ending and accepting deposits. Consequently, if the regulations reduce the reserve fraction, the multiplier effect is enhanced significantly.
Pros and Cons of Monetary Policy As Opposed To Fiscal Policy for Economic Policies and Practices Implementation
The monetary policy refers to the activities that the central bank carries out to influence the supply of money. Fiscal policies refer to the decisions that governments make about taxation and expenditure. The two policies are utilized to regulate the economy. Both are made to create an economic environment that is stable and positive in terms of growth. Monetary policies are ideal for encouraging investments among consumers, especially when interest rates are reduced. In addition, they can lead to low interest on mortgage payments which increases the clients’ ability and power to spend; they are also easily predictable and transparent. Monetary policies enable the promotion of stable prices, thus ensuring that the rates of inflation gain stability. However, monetary policies do not guarantee recovery from recessions and take time to implement. They could also discourage the expansion of businesses when the interest rates increase (CFA Institute, 2022).
Summary of Findings
- Money must store value, enable exchange, possess liquidity, and serve as a unit of account.
- The Fed is responsible for monitoring the country’s money supply.
- The FOMC meets every six weeks to review the economy and make policies.
- Banks do not lend out all the money; they retain some fractions of the deposits in reserves.
- Lending and deposits create a multiplier effect.
- Loans create liabilities for consumers.
- Monetary policies are easier to use compared to fiscal policies.
References
CEIC Data. (2021). United States Money Supply M1. Retrieved from CEIC: https://www.ceicdata.com/en/indicator/united-states/money-supply-m1
CFA Institute. (2022). Monetary and Fiscal Policy. Retrieved from https://www.cfainstitute.org/en/membership/professional-development/refresher-readings/monetary-fiscal-policy
Mankiw, N. G. (2021). Brief Principles of Macroeconomics. Cengage.
ORDER A PLAGIARISM-FREE PAPER HERE
We’ll write everything from scratch
Question
The monetary system in any economy facilitates trade and allows people to trade more efficiently, as compared to a barter economy. In the United States, the monetary authority is the Federal Reserve System (also referred to as the Federal Reserve, or informally, as the “Fed”.)
Discussion – The Monetary System
For this assignment, use the information presented in the textbook and the Fed’s website (http://www.federalreserve.gov/) when addressing the questions below.
What are the requirements for something to be considered money? Why does the dollar have value?
What does the money supply consist of, and what are the respective amounts in the total money supply for the United States?
What are the primary functions of the Fed? What role does the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) play in our economy?
What role do the financial institutions (commercial banks and other institutions) play in our financial system?
What is meant by the term “fractional-reserve banking” in our system? What are the implications for consumers?
What are the tools available to the FED for controlling the money supply? Which are used most often? Which are most effective?
How does the money multiplier help to determine the effects of monetary policy?
What are the pros and cons of using monetary policy, as opposed to the use of fiscal policy, for implementing economic policies and practices?
Deliverables:
Prepare a 5-6 page Microsoft Word document that addresses the above-noted concerns and meets APA standards.
Include a summary section in your report that contains 5-7 bullet points identifying your major findings or conclusions of your paper.
Submit the summary section as your initial post in the Discussion Area by the due date assigned. Include the full report as an attachment to your posting.
Continue your discussions until the end of the week by commenting on at least two other submissions by your peers and identifying the strengths and weaknesses of each post.