Develop Service Process Improvement Recommendations
Introduction – describe what you intend to do and how you will approach the task.
This process intends to observe the processes involved in visiting my physician for a flu shot, checking areas of potential waste and developing service process improvement recommendations. The task must be approached with an open mind and some level of keenness and observation. I will, therefore, visit the physician on working days and take note of the processes involved in getting treatment in the hospital.
Do you need an Original copy of “Develop Service Process Improvement Recommendations”? Contact us
A simple flow chart that maps the sequence of operations for variants #1 and #2 above. While you may need to make certain assumptions in your description of variants #1 and #2, your process map should include, at a minimum, all components of the process that are visible to the patient. You may combine your analysis of the first two variants due to a lack of information.
Flow Chart: Variants 1 and 2
This first process shows the flow chart that is formally defined and written in the business document. It also combines the process that everyone generally believes exists. The components are the basic ones that are visible to a patient. When patients arrive, they go to the reception and issue their details. The receptionist checks if their details are available in the system; if not, they are registered in the healthcare system database. After which, they are directed to an adjacent nurse’s office. If the nurse has another patient, the arriving patients wait in the waiting room. When their turn comes, the nurse takes their pulse, weight, blood and urine sample. The nurse then sends them to the doctor’s office. If the doctor is available, the patient can have an immediate session with the doctor. Otherwise, the patient waits in the waiting room for their turn. The doctor can then have a session with the patient if it’s their turn; the doctor makes any diagnosis and gives the flu shot. If the doctor needs to see the patient again, they make an appointment. Otherwise, the patient is sent to the pharmacy for the necessary prescriptions. The patient then leaves.
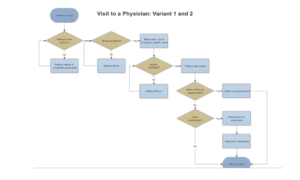
Variants 1 and 2
Potential problems or waste
Failure of care delivery
This waste may result from the poor execution of the best care practices, safety systems and practices aimed at preventive care (Berwick & Hackbarth, 2012). This may result in terrible clinical outcomes, leading to money loss.
Failure of care coordination
This waste may result from patients experiencing fragmented care, resulting in complications and readmissions. This can be seen when the patient has to go to the nurses and doctors separately.
Long waiting times
This waste results from the patients waiting long to receive patient care. This situation is even longer because the patients must wait for the nurse and the doctor.
Follow Chart: Variant 3
This flowchart shows the process that exists in the health facility. It is similar to the first variant, although the nurse does not see the patient before the doctor. When patients arrive, they go to the reception and issue their details. The receptionist checks if their details are available in the system; if not, they are registered in the healthcare system database. After which, they are directed to an adjacent doctor’s office. If the doctor is available, the patient can have an immediate session with the doctor. Otherwise, the patient waits in the waiting room for their turn. The doctor can then have a session with the patient if it is their turn; the doctor makes any diagnosis and gives the flu shot. If the doctor needs to see the patient again, they make an appointment. Otherwise, the patient is sent to the pharmacy for the necessary prescriptions.
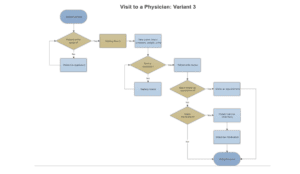
Variant 3
Potential problems or waste
Failure of care delivery
This waste may result from the poor execution of the best care practices, safety systems and practices aimed at preventive care. This may result in terrible clinical outcomes, leading to money loss.
Waiting times
This waste results from the patients waiting long to receive patient care. In this situation, the patients must wait for the doctor.
Flow Chart: Variant 4
This last process shows the flow chart that should exist to deliver what the customers want. The patient makes an appointment, and when they arrive, they go to the reception and issue their details. The receptionist checks if their details are available in the system; if not, they are registered in the healthcare system database. After which, they are directed to an adjacent doctor’s office that is not busy. If one of the doctors is available, the patient can have an immediate session with the doctor. Otherwise, the patients wait in the waiting room for their turn in case all the doctors are busy. One of the doctors can then have a session with the patient if it is their turn; the doctor makes any diagnosis and gives the flu shot. If the doctor needs to see the patient again, they make an appointment. Otherwise, the patient is sent to the pharmacy for the necessary prescriptions. The patients can then leave at their will.
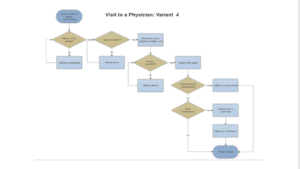
Variant 4
Potential problems or waste
Failure of care delivery
This waste may result from the poor execution of the best care practices, safety systems and practices aimed at preventive care (Berwick & Hackbarth, 2012). This may result in terrible clinical outcomes, leading to money loss.
From the list of successful techniques for eliminating waste in service companies in this week’s readings, select three that you feel are appropriate in shaping your recommendations for improvement in the doctor’s service process. For each of the three techniques, briefly describe what would need to take place.
Inventory management to reduce the impact of drug shortages
This technique presents a way to cope with inevitable drug supply disruptions. If an item is crucial, then more stock should be held. The method finds the optimal levels of stock and the quantity levels of the order to reduce the total costs, minimizing disruptions that may affect supply (Saedi, Kundakcioglu & Henry, 2016). The other conventional methods consider the tradeoffs between the costs and the optimal solution. The pharmaceutical supply chains are unique because of attributes such as zero fixed-cost ordering, zero lead time, item substitution, supply disruption, and the focus on service levels, leading to a high warehouse utilization independent of the size. This technique, therefore, tries to find the balance between the space the items occupy and the disruption rate, the expected disruption duration, demand, and the disruption rate of the substitute items. The proposed technique will be better than the existing healthcare inventory management policies. The only exception would be the holding costs resulting from low space utilization (Saedi, Kundakcioglu & Henry, 2016). This technique also proposes stocking items with more than one substitute. A substitute may not always be as adequate as the mainstream drug. However, this would ensure the patients can always access the required medicines.
Supply Chain Management
The healthcare industry has been slow to embrace the management practices of supply chain management practices. There are some reasons why healthcare lag behind in supply chain management and the things that can be done to improve efficiency in the supply chain (Fibuch & Ahmed, 2015). The supply chain is more than merely controlling inventory. It relates to supply chain performance, network design, agility, and integration (VanSchenkhof, Baker & Cox, 2015). A different approach must be considered when managing the supply chain in healthcare because of its significant impact on the organization. Modern supply chain practices involve creating trust and collaborating with the suppliers, implementing best practices and implementing these best practices in the organization. Modern healthcare must align with the supply chain. Additionally, it must make other components systematically aligned with the supply chain, such as robust information systems and quality management systems which drive the supply chain.
Integrating the supply chain with Total Quality Management ensures the future competitiveness of healthcare (Fibuch & Ahmed, 2015). Additionally, the quality practices are significantly related to the participation of the supplies, which translates to better supply chain performance. The supply chain performance substantially influences the cost structure of healthcare. Inefficiencies in the supply chain cause a loss of finances by increasing the costs of operating the supply chain. The preference for items by physicians increases expenditures by up to 40 per cent (Fibuch & Ahmed, 2015). The proper management of the supply chain will therefore mitigate any unwanted spending.
Waste specific Reduction
To bring healthcare costs into a sustainable range for private and public players, healthcare organizations must implement programs to cut costs. The agenda should reduce the levels of payment, benefit eligibility and structure. The strategy should be less harmful to minimize waste to the value-added care. The system should focus on the sics waste categories: over-treatment, failures of care coordination, failures in the execution of care processes, administrative complexity, pricing failures, and fraud and abuse (Berwick & Hackbarth, 2012). These healthcare wastes comprise twenty per cent of healthcare expenditures or more. A strategy that aims to handle these wastes specifically has the potential to achieve considerable reductions in price. However, implementation of such a strategy requires thorough evaluation because it may cause economic dislocations.
Other Related Post: Theory of Justice As Fairness
References
Berwick, D. M., & Hackbarth, A. D. (2012). Eliminating waste in US health care. 307(14):1513– 1516. doi:10.1001/jama.2012.362.
Fibuch, E., & Ahmed, A. (2015). Health Care’s Supply Chain: Issues to Consider. Physician Leadership Journal, 2(6), 26-30.
Saedi, S., & Kundakcioglu, O. E., & Henry, A. (2016). We are mitigating the impact of drug shortages for a healthcare facility: Inventory management.
VanSchenkhof, M., Baker, D., & Cox, J. (2015). Inventory Management at the Theme Park. Journal of Critical Incidents, 890-92.
ORDER A PLAGIARISM-FREE PAPER HERE
We’ll write everything from scratch
Question
Week 6 – Assignment: Develop Service Process Improvement Recommendations
Instructions
Your primary care physician operates a sound business practice that sometimes seems to suffer from several forms of waste. As a dedicated patient engaged in the study of operations management, you are in a unique position to offer an analysis of your doctor’s business operation and provide recommendations for improvement.

Develop Service Process Improvement Recommendations
Consider the common interpretation of service processes in use at many organizations, which is used to identify four variants of a service process:
- The process is formally defined and recorded in a business document.
- The process that everyone generally believes exists.
- The process as it exists.
- The process that should exist to deliver what the customer wants.
Using your arrival at the doctor’s office as a starting point, create a document that focuses on visiting your doctor for a flu shot. Be sure your document incorporates the following:
- Introduction – describe what you intend to do and how you will approach the task.
- A simple flow chart that maps the sequence of operations for variants #1 and #2 above. While you may need to make certain assumptions in your description of variants #1 and #2, your process map should include, at a minimum, all components of the process that are visible to the patient. You may combine your analysis of the first two variants due to a lack of information.
- A flow chart that maps the process that exists (variant #3).
- A flow chart that maps the process according to variant #4, as you believe it should be.
- Above each flow chart, include a paragraph describing the critical process components and identify potential problems or elements of waste in the process map that follows.
From the list of successful techniques for eliminating waste in service companies in this week’s readings, select three that you feel are appropriate in shaping your recommendations for improvement in the doctor’s service process. For each of the three techniques, briefly describe what would need to take place.
Complete your paper with a list of three recommended changes, noting the timeframe within which each might be completed and the expected benefit(s) to the doctor’s practice resulting from implementation.
Length: 5-7 pages, not including assignment cover sheet, title page, and reference page(s). Use topic section headings for each criterion listed above.
Your response should demonstrate thoughtful consideration of the ideas and concepts presented in the course by providing new thoughts and insights relating directly to this topic. Your answer should also reflect professional business writing and current APA standards. Be sure to adhere to Northcentral University’s Academic Integrity Policy.

