Comprehensive Security Management Plan – Englewood Health Care
Organization Overview
Englewood Health Care is a healthcare facility that services a broad metropolitan area region. The organization comprises several units that provide a wide range of medical services, including urgent care, diagnostic services, primary care, surgery, and rehabilitation programs. The facility is medium-sized, with 500 employees, including physicians, registered nurses, administrative personnel, security personnel, IT specialists, and other support staff.
Key Information
-
- Organization Type: Healthcare facility (hospital, outpatient services)
- Englewood, New Jersey, with multiple satellite locations
- Sector: Health services (medical, emergency, outpatient, rehabilitation)
- Services Provided: Primary care, urgent care, specialist consultation, diagnostic services, surgeries, rehabilitation, and wellness programs.
- Relevant Security Issues: Protection of patient data (HIPAA), physical security of the facilities, cybersecurity of medical records, and compliance with industry regulations.
Chart
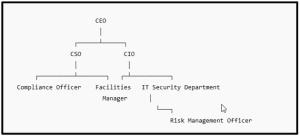
Chart 1: Englewood Health Care Organizational Structure
Security Working Group (WG) Structure and Ties
The Security Working Group (WG) is a component of the organizational hierarchy, comprising representatives from various departments. The working group is fundamental to the organization’s security, with the Chief Security Officer (CSO) as the primary point of contact. The members of the WG work on various projects related to security, both physical and digital, as well as compliance, risk management, and other multidisciplinary fields.
Members of the WG
- CSO (Lead of WG) – Directs security operations and drives interdepartmental collaboration on security activities.
- CIO – Collaborates with other departments to develop and implement cybersecurity strategies.
- Compliance Officer – Monitors organizational compliances to set regulations and patterns of the industry.
- Facilities Security Manager – Deals with the implementation of security policies in healthcare facilities (Force & Initiative, 2013).
- Risk Management Officer – Evaluates security risks in cybersecurity, physical security, and other associated compliance concerns.
This group integrates security to make certain that all healthcare organization’s operations and activities are secure and safe.
Memo: Information Exchange between Security Working Group (WG) and Other Units
To: CEO, CSO, IT, Facilities, Legal and Compliance
From: CSO Englewood Health Care
Subject: Information Exchange on Security Management
Date:
For security issues pertaining to risk management of Englewood Health Care, there are information flow gaps as far as communication is concerned. Below is the communication flow that has to be followed.
Incident Reporting
All possible security and compliance risk issues will be escalated to the CSO by the other department heads, such as IT, Facilities, and Risk Management. If such an incident occurs, the CSO will, in turn, report it to the CEO.
Security Updates
The CSO will hold Regular Meetings with the Security Working Group, which consists of IT, Legal, Facilities, and Risk Management representatives. Ongoing security issues and assessment of risks and compliance challenges will be discussed.
Cross-Departmental Collaboration
The CIO will coordinate with the Facilities Security Manager to integrate procedures for both physical and electronic security. Additionally, any compliance matters, such as HIPAA, will be addressed directly by the Compliance Officer and the Chief Security Officer (CSO).
Escalation Process
For security breaches or gaps that are regulatory, the CSO has the authority to bring these matters directly to the CEO’s attention for quick resolution. This way, the executive branches have full knowledge of very critical security or compliance issues.
Policy Updates and Risk Mitigation
New policies regarding security, risk mitigation, and organizational compliance will be communicated by the Chief Security Officer (CSO) to the whole organization. Each department will ensure that the lower-level units or sub-units within those units receive this information through their department heads (Walsh, 2023).
Week 2: Security Business Requirements
In today’s healthcare environment, the security of sensitive patient information is a central need for ensuring compliance with legal and ethical standards. Englewood Health Care must have a process improvement plan as a management system to enhance its security posture. The Capability Maturity Model Integration (CMMI) framework provides a model for process improvement at the organizational level. In this model, the Risk Management process area (PA) is of utmost importance for healthcare security.
Overview of the CMMI Framework
CMMI is a model for process improvement that offers a structured approach for an organization to follow in developing, managing, and improving its processes. Like other sectors, healthcare has widely embraced this model because organizations are aided to attain desirable standards of performance maturity. The framework rests on specific and generic practices aimed at continuous improvement. Englewood Health Care can improve its security management practices by using CMMI and conforming to recognized standards and guidelines for the identification, evaluation, and mitigation of risks (Beth et al., 2006).
Risk Management in Healthcare Security
As part of the CMMI framework, the Risk Management PA is key for identifying, evaluating and triaging potential risks that may undermine the organization. Healthcare facilities such as Englewood Health Care are at risk of facing complex security issues like cybersecurity and physical security threats. With the criticality of information required for compliance with several regulations, especially HIPAA, managing risk becomes a vital element of the overall security management plan.
Specific Practices of the Risk Management Process Area
The Risk Management PA relies on a defined set of practices aimed at standardizing the procedures for capturing and mitigating risks within an organization:
- Risk Identification: This practice entails the comprehensive identification of risks associated with cybersecurity, physical security, and compliance with laws and regulations. Risks are classified according to their source and what level of damage they can cause to the organization. This method allows the organization to direct its efforts towards the most threatening risks.
- Risk Evaluation: After identifying risks, every risk has to be assessed on their probability of occurrence and the seriousness of the impact. This evaluation step is necessary in order to rank the risks and decide how much effort needs to be put into each risk management plan.
- Mitigation Strategy Development: There is risk-specific strategy development aimed at either eliminating or reducing defined risks. For instance, in a healthcare setting, the policies and staff training serve as mitigation strategies to enhance cyber security, physical security, and staff training regularly.
- Implementation and Monitoring: This step involves implementing the risk mitigation strategies and measuring their effectiveness on a continuous basis. From regular auditing and reviewing, any new risks that emerge can be dealt with alongside ensuring that the mitigation works through time.
Generic Practices Supporting Risk Management
Alongside specific practices, the CMMI framework has generic practices to support an organization’s need for continuous risk management. Set policies define responsibility and even devise ways of assessing activity accomplishment are some practices outlined. Englewood Health Care is a clear example with sharp reporting lines (Moore, 2023). For example, risks deemed important by the Chief Security Officer (CSO) are reported directly to the CEO to ensure that risk management strategically permeates the organization.
Integration into the Comprehensive Security Management Plan
The incorporation of Risk Management PA into the Comprehensive Security Management Plan provides a cohesive approach to security risks. This integration deals with both short and long-term risks in a preventive manner. With CMMI, an organization is able to improve security practices on emerging, evolving problems, which helps ensure operational resilience and protection of sensitive patient information. This type of integration is proven to also be in accordance with enterprise standards while capturing the main objective of enabling safe and well-organized healthcare service delivery.
TBD
Week 4: System Design Principles
TBD
TBD
References
Beth, C. M., Konrad, M., & Shrum, S. (2006). CMMI: Guidelines for process integration and product improvement. Addison-Wesley Professional. https://insights.sei.cmu.edu/library/cmmi-for-development-guidelines-for-process-integration-and-product-improvement-third-edition/
Force, J. T., & Initiative, T. (2013). Security and privacy controls for federal information systems and organizations. NIST Special Publication, 800(53), 8-13. http://dx.doi.org/10.6028/NIST.SP.800-53r4
Moore, C. (2023). Health information technology. In Chronic Illness Care: Principles and Practice (pp. 481–495). Cham: Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-29171-5_37
Walsh, A. P., Hamill, S., & Morrison, I. (2023). Health information technology. In Jonas and Kovner’s Health Care Delivery in the United States (13th ed., p. 359). Springer Publishing Company.
ORDER A PLAGIARISM-FREE PAPER HERE
We’ll write everything from scratch
Question
Comprehensive Security Management Plan – Englewood Health Care
Description
Continue development of the Comprehensive Security Management Plan. This second section will be (2) pages to assess security business requirements. After a summary of the capability maturity model integration (CMMI), the process area (PA) of the CMMI model that is considered to have the highest importance to the project security requirements will be identified and defended. The PA, its goals, the specific practices, and the generic practices will be part of the justification.

Comprehensive Security Management Plan – Englewood Health Care
The project deliverables are the following:
Update the Comprehensive Security Management Plan document title page with the new date.
Update the previously completed sections based on the instructor’s feedback.
Use the subtitle “Security Business Requirements.”
Summarize the CMMI.
Identify and defend the PA of the CMMI model for your chosen organization.
The PA, its goals, the specific practices, and the generic practices will be part of the justification.
Be sure to update your table of contents before submission.
Name the document “yourname_CS654_IP2.doc.”