Balanced Scorecard
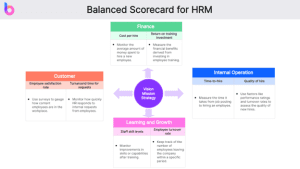
A balanced scorecard is a multipurpose managerial tool used by organizations for performance management and strategy implementation effectiveness. The tool enables an organization to implement action plans that will enable it to achieve its goals (Tawse & Tabesh, 2023). In other words, a balanced scorecard enables an organization to come up with strategic fit processes to enable the organization to achieve its goals.
For instance, if an organization seeks to achieve cost leadership, the balanced scorecard will offer an insight into processes and learning-related measures it will implement to attain cost leadership (Tawse & Tabesh, 2023). Some of the processes that may enable a company to achieve cost leadership may include laying off some employees and enhancing performance management. Through the BSC, top managerial teams capture the company’s desired aspirations, enabling them to channel their efforts and knowledge into the right course.
Given the important role a balanced scorecard plays in performance management, it can be applied by the HR department to enhance productivity. Firstly, it offers insight into action steps that an organization may implement to achieve its HR mission and vision. Although most organizations do not have an official HR mission, they come up with an unofficial mission to help them improve their human capital.
For instance, an organization’s mission may be ‘To foster a collaborative and highly skilled workforce.” The balanced scorecard will offer an insight into actions the organization may undertake to achieve this goal, including offering competitive compensation packages, ensuring there is an effective culture map, and the right skills to achieve the goal.
Additionally, a balanced scorecard captures the aspirations and needs of the company’s HR customers. Customers in this case are either business units/departments or employees. On the one hand, business units/departments desire timely hires, the best talent, and an effective partnership with the HR department (Chavan, 2009). On the other hand, employees look up to the HR for fair compensation, training and development initiatives, and employee satisfaction (Chavan, 2009).
Based on the feedback collected from the two units (customers), the organization will implement processes that facilitate them to attain their goals, including implementing training initiatives, culture training, and filling key jobs. An organization’s culture takes a long time to change; hence, it requires deep thought and patience.
Moreover, the balanced scorecard aids top executives in matching people with jobs. One of the steps top organizational managers use to create position profiles is by identifying the criteria that define superior or effective performance (Chavan, 2009). Some hard outcomes, such as sales and profit data, can be used by line managers to identify performance levels. A balanced scorecard will offer insight into performance effectiveness, enabling the HR department to place the right people in different positions.
HR Operating Metrics
HR Operating Metrics offer an insight into the performance and effectiveness of the HR function in the organization. One of the aspects of HR Operating Metrics is the HR routine metrics, which monitor day-to-day operations, identify short-term problems, and ensure effective decision-making. On the other hand, the HR strategy metrics focus on an organization’s long-term goals.
A good example is employee engagement, which influences organizational performance in the long run. The HR organizational oversight metrics delve into governance and compliance of the HR function, thus shielding the organization from unnecessary legal risks.
AHROP Metrics
AHROP metrics refer to how an organization attracts, hires, retains, and protects its reputation as an organization’s HR function. Regarding the routine HR metrics, the application rate can offer insight into whether individuals are interested in working for a company, offering an insight into whether the company has created the right environment to attract top talent (Wallace et al., 2014). Besides, strategic metrics on AHROP give insight into an organization’s quality of hires and level of engagement. On the other hand, oversight metrics, when applied to an organization’s AHROP, will offer insight into diversity application and the retention risk for specific diversity roles.
HR Oversight Metrics
The HR oversight metrics delve into the governance structures of the HR function. Among others, it seeks to establish whether the committees set up to guide decision-making are effective, and if the people making delegated decisions are doing the right thing (De Smet, 2015). Processes are extremely important because, apart from internal performance, organizations are monitored externally, something that can affect their reputation among other stakeholders (De Smet, 2015).
One of the oversight stakeholders is governments in jurisdictions within which a business operates. The business must put in place specific metrics that ought to be attained for it to be in good standing with the government and preserve its reputation to attract top talent.
References
Chavan, M. (2009). The balanced scorecard: a new challenge. Journal of Management Development, 28(5), 393–406. ResearchGate. https://doi.org/10.1108/02621710910955930
De Smet, A. (2015, December 1). The keys to organizational agility. McKinsey & Company. https://www.mckinsey.com/capabilities/people-and-organizational-performance/our- insights/the-keys-to-organizational-agility
Tawse, A., & Tabesh, P. (2023). Thirty Years with the Balanced scorecard: What We Have Learned. Business Horizons, 66(1), 123–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bushor.2022.03.005
Wallace, M., Lings, I., Cameron, R., & Sheldon, N. (2014). Attracting and Retaining Staff: The Role of Branding and Industry Image. Workforce Development, 19–36. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-4560-58-0_2
Appendix A
Appendix B
Metric(Name of Metric) |
Formula(Numerator/Denominator) |
% Met or Exceeded*
|
|
| HR Operating Metrics | 1. Filling time | Duration to fill positions/ Total positions filled | |
| 2. Cost per hire | Total recruitment cost/Total number of hires | ||
| 3. Training duration per employee | Total training hours/total employees trained. | ||
| AHROP Metrics | 1. Offer acceptance rate | Number of accepted offers/Offers extended | |
| 2. Turnover rate | Resignations/Total workforce | ||
| 3. Rate of promotion | Total promotions/filled posts | ||
| 4. New employee retention rate | Number of hires post-first year/total new employees | ||
| HR Oversight Metrics | 1. Diversity employment rate | Hires from minority groups/Total employees | |
| 2. Policy compliance rate | Compliant units/Audited units | ||
| 4. Alignment with goals | HR initiatives that comply with strategic goals/Total HR initiatives |
ORDER A PLAGIARISM-FREE PAPER HERE
We’ll write everything from scratch
Question
For this Assignment, you will focus on creating the Balanced Scorecard.
You have studied the use and impact of metrics to monitor and trend outcomes as contrasted with targeted outcomes and compared oftentimes with industry standards. Typically, the Human Resources Department/Division has HR metrics that are: (1) routine HR metrics, (2) metrics to track the HR strategies in their AHROP, and (3) oversight metrics for organizational performance that they oversee, but do not own (e.g., metrics that examine the overall success of the organization in some way and typically are organizational knowledge [training and development], organizational capacity [hiring, staffing, and retention], employee relations [Title VII-related issues], and organizational effectiveness [performance management and measurement]).
The Human Resources Department/Division not only directs and monitors its own department’s areas of responsibility (HR Routine Metrics), but it also tracks and trends larger more strategic organizational oversight metrics which impact the entire organization and drive the organization’s success. These are metrics upon which the CEO and COO are very dependent to assess progress and, at times, necessary redirection.
*Keep in mind that a Balanced Scorecard does not contain ALL of HR’s metrics—just the top 10 or fewer, which also are often shared, even publicly.
For this Assignment, review the week’s Learning Resources and consider the role of HR metrics in monitoring and trending the three categories contained in the attached HR Metrics Matrix.

Balanced Scorecard
In a 2- to 3-page paper compile monitoring and metric information, including the following:
- Introduce the concept of the Balanced Scorecard and briefly discuss how it is used in organizations and specifically how it is used in HR, both daily and strategically. Using the Walden Library or other online resources, provide a sample HR Scorecard and place it in Appendix A.
- Create section headings in the paper for the key HR metrics, one for each of the three categories identified in the attached Matrix and discuss: Routine HR Metrics, HR Strategy Metrics, and HR Organizational Oversight Metrics.
- Provide an analysis supported with rationale for including the metrics chosen on your Balanced Scorecard.
- Create an HR Balanced Scorecard, as a Table placed in an Appendix B, using the attached required Matrix and tailoring it to the HR Department/Division of the organization you have chosen for your Annual Human Resources Operating Plan.
Aghina, W., De Smet, A., Murarka, M., & Collins, L. (2015, December 1). The keys to organizational agility. [Multimedia file]. McKinsey & Company. https://www.mckinsey.com/
Blain, N., Royal, M., & Stark, M. J. (2018, December). Here’s how to build organizational agility. Human Resource Executive. https://
- This order is related to Orders 60359 (Week 1) and 60397 (Week 2) – (Shared in this Link)
- The chosen organization is Apple Inc.
- Please check all the attachments