Investing in Workplace Safety: A Strategic Loss Prevention Initiative
Occupational injury is a chronic problem for firms, which leads to loss of money, loss of productivity, and even litigation. The risk managers need to invest in a good quality loss prevention program so that such risks can be handled. Employee Ergonomics Program is one such program which has been instituted for prevention of musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs) and other occupational injuries. The objective of this program is to maximize work facility design, incorporate ergonomic training, and maintain policies of support that are directed at reducing the frequency of injury and the associated cost: Investing in Workplace Safety: A Strategic Loss Prevention Initiative.
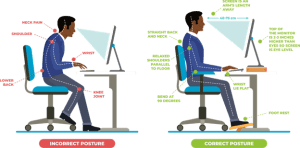
A properly designed ergonomic workstation can significantly reduce the risk of MSDs (The Natural Posture, 2024)
Background, Goals, and Needs of the Ergonomics Initiative
The Employee Ergonomics Program is designed to address the high incidence of workplace injuries related to poor posture, repetitive motion, and inadequate workstation design. According to the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA, 2022), MSDs account for nearly 33% of all workplace injuries, leading to increased workers’ compensation claims and lost workdays.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) defines ergonomics as “the science of fitting workplace conditions and job demands to the capabilities of the working population” (CDC, 2024). Implementing proper ergonomic practices helps prevent work-related MSDs, which are injuries or disorders of the muscles, nerves, tendons, joints, cartilage, and spinal discs.
The primary goals of this initiative include:
- Reducing workplace injuries by 30% within two years
- Lowering workers’ compensation claims related to MSDs
- Enhancing employee productivity and job satisfaction by improving workplace ergonomics
- Increasing organizational compliance with OSHA and industry-specific safety regulations
The program requires financial investment in ergonomic workstations, specialized training, and assessment tools to evaluate and enhance workplace safety.
Primary and Secondary Funding Sources
To finance the Employee Ergonomics Program, organizations must secure funding from various sources.
Primary Funding Sources:
- Workers’ Compensation Base Accrual Rates: A portion of the workers’ compensation premiums can be allocated to proactive loss prevention strategies
- Internal Safety Budget Allocation: Many organizations set aside funds for safety and health programs to meet regulatory compliance and reduce injury-related costs
- Government Grants: The United States Department of Labor (2023) has a range of funding programs in their grants, such as funding to enhance the safety of workplaces
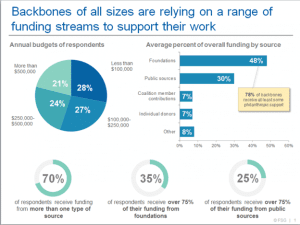
Typical distribution of funding sources for ergonomic initiatives (Sullivan et al., 2019)
Secondary Funding Sources:
- Private Insurance Rebates: Some insurance companies provide rebates or premium discounts to companies that actively work toward eliminating risks at the workplace.
- Collaborations with Ergonomic Equipment Suppliers: Deferred payment or subsidized loans are provided by suppliers for ergonomic workstation installations
- Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) Initiatives: Firms mostly attribute investments in safety at the workplace to CSR initiatives, budgeting for it as part of total sustainability and workers’ health initiatives
Funding Constraints and Structuring the Financial Plan
While these sources of funding provide financial support, several limitations may be faced:
- Budget Constraints: Internal budgets may not accommodate any new projects, requiring diversion from other funds
- Approval Processes: Grants or insurance rebates involve stringent documentation and compliance with specific guidelines
- Return on Investment (ROI) Justification: Management may require feedback on expected cost savings before the release of funds
To successfully manage these sources of funding, organizations should:
- Conduct cost-benefit analysis to determine the economic returns on ergonomics investment
- Seek government and industry grants in advance to supplement internal funding sources
- Phase the program, starting with departments at high risk to demonstrate success and secure further funding
- Work together with suppliers to get cost-effective solutions, i.e., lease ergonomic equipment instead of purchasing outright
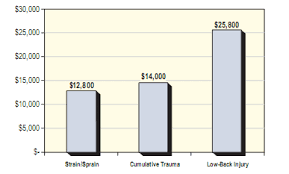
Typical return on investment timeline for ergonomic initiative implementation (Ip, n.d.)
Internal Ramifications and Management Strategies
When an ergonomics program is implemented, internal problems arise in the form of:
- Resistance to Change: Employees may be opposed to new work habits
- Solution: Conduct workshops to show advantages of ergonomic work habits and provide incentives for participation
- Budgetary Concerns: Other than the safety department, other departments may be opposed to expenditures
- Solution: Highlight how cost savings from injury equate to overall organizational savings
- Monitoring and Compliance: Staying current on ergonomic standards is a critical ongoing activity
- Solution: Hire a safety officer to oversee implementation, conduct regular audits, and include ergonomic training as part of new hire orientation
The CDC (2024) recommends an integrated model to the adoption of an ergonomic program like risk assessment, hazard prevention and control, health management, education and training, and evaluation of the program.
Conclusion
Investment in Employee Ergonomics Program is a risk management department’s strategic move. Through the availability of different sources of funds, setting up financial arrangements in the suitable form, and pre-identification of internal challenges, organizations are in a position to reduce on-the-job injuries significantly, enhance workers’ well-being and health, and experience financial gains in the long term. Risk management directors should implore such programs to create a healthier, more secure working environment.
Learn about efficient ergonomic program execution by consulting OSHA’s Ergonomics Resources or exploring Department of Labor Grant Opportunities.
References
CDC. (2024, May 12). Ergonomics and Work-Related Musculoskeletal Disorders. Ergonomics and Musculoskeletal Disorders. https://www.cdc.gov/niosh/ergonomics/index.html
Ip, W. (n.d.). ROI of Ergonomic Improvements: Demonstrating Value to the Business. Retrieved March 10, 2025, from https://aeasseincludes.assp.org/proceedings/2009/docs/729.pdf
OSHA. (2022). Ergonomics – Overview | Occupational Safety and Health Administration. Www.osha.gov; Occupational Safety and Health Administration. https://www.osha.gov/ergonomics
Sullivan, E., Juster, J. S., & dylan. (2019, June 21). Securing Funding for the Collective Impact Backbone Role: Lessons from the Field – Collective Impact Forum. Collective Impact Forum. https://collectiveimpactforum.org/blog/securing-funding-for-the-backbone-role-lessons-from-the-field/
The Natural Posture. (2024). Guide to Creating an Ergonomic Workstation at Home. The Natural Posture. https://thenaturalposture.com/blogs/news/guide-to-creating-an-ergonomic-workstation-at-home
U.S. Department of Labor. (2023). Grants for 2023. DOL. https://www.dol.gov/agencies/eta/grants/2023
ORDER A PLAGIARISM-FREE PAPER HERE
We’ll write everything from scratch
Question
DHA 715 Week_4_Assignment
Risk management includes a funding mechanism that stimulates investment in loss prevention and loss control measures to reduce the cost of risk. Funding may be obtained through a percentage of workers’ compensation base accrual rates. Investing in loss prevention reduces claim frequency, which has a positive effect on severity and overall claim exposure. An appropriate tracking system documents losses or exposure prior to initiating the new program and, after a selected time, documents the effect of the program on losses or exposure.
Imagine this scenario: You’re writing a blog post for a blog site whose readers are heads of risk management departments.

Investing in Workplace Safety: A Strategic Loss Prevention Initiative
Select 1 loss prevention initiative from your own experience or from peer-reviewed scholarly sources.
Write a 550- to 700-word blog post that analyzes your selected loss prevention initiative. In your blog post:
- Summarize the background, goals, and needs of your selected loss prevention initiative.
- Identify the loss prevention initiatives:
- Primary and secondary funding sources
- Funding constraints for each source
- Describe a plan to structure these funding sources to meet the initiative’s goals.
- Specify the potential internal ramifications that may arise when implementing the loss prevention initiative and your plan for managing the ramifications.
Include relevant visuals and external website links to support the initiative.
Cite the references and visuals you used to support your assignment.