Global Lack of Education Due To Poverty
Introduction
Education plays a significant role in preparing people for their future by equipping them with the knowledge and skills required to compete for jobs and venture into entrepreneurship. The issue of lack of education has gained the attention of various scholars and researchers because of the rise of illiterate people, especially in developing countries. Existing studies suggest that the government is responsible for addressing the issue because it allocates the resources needed in the education sector and regulates the education fees in the public sector, thus contributing to education affordability. Communities in different countries worldwide are also taking the initiative to mobilize members to take their children to school to eradicate poverty and poor living conditions. It is important to understand the issue of lack of education to design effective measures to eliminate it. Lack of education is also a leading cause of inequality in most societies; hence, there is a need to understand its causes, impacts, and solutions. The impact of lack of education in developing countries indicates that lack of education is a serious issue that contributes to slow development in the affected societies, hence the need to actively engage the community members, parents and guardians, and local leaders in policymaking and education reforms to ensure that all children in the community acquire basic education. Lack of education is a serious issue that contributes to slow development in the affected societies, hence the need to actively engage the community members, parents and guardians, and local leaders in policymaking and education reforms to ensure that all children in the community acquire basic education.
Background Information
Poverty is among the issues affecting most societies in developing countries. According to Bhargava (2006), poverty includes non-income dimensions such as the prevalence of diseases, health, education, gender equality, and access to sanitation and water. The solution to the widespread poverty in developing countries is quality formal education that can fill the skills and knowledge gaps. The link between poverty and lack of education has been documented by various researchers who focus on how poverty limits a person’s ability to afford to pay school fees, the impact of poverty on a person’s willingness to study, and the role of poverty in decreasing a person’s readiness to join school due to aspects such as home life and neighborhoods. According to Ferguson et al. (2007), the main poverty-related factors that affect a child’s development and readiness to join school include poverty depth, incidence, timing, duration, and community attributes such as crime and poverty concentration in a neighborhood. Children from low-income families also usually lack the stimulation to learn and are not eager to acquire the social skills needed to prepare them for the learning environment because they are more focused on helping their families earn an income.
The relationship between poverty and lack of education is also evident in developed countries. A study conducted by Ferguson et al.(2007) in Canada to access the relationship between poverty and education established that poverty has a negative impact on academic achievement because of poverty-related risk factors such as high family stress and limited parental education. Poverty is also the leading cause of school dropouts, especially in developing countries where students may be required to look for a job to meet their basic needs and support their families. According to Ewiss (2020), the dropout rate of enrolled children is linked to poverty because low-income families use their children to increase their income by sending them to work. Most low-income families living in extreme poverty are also unable to meet the expenses associated with enrolling one or all of their children in schools (Mihai et al., 2015). The author adds that poverty also makes most people think they will fail in education, implying that children born into poverty cannot escape poverty. Children born in poverty are also unprepared to attend school because they struggle to integrate. Further, Hen (2022) argues that the lack of economic investment, especially in developing countries, has led to the inability of most countries to create sufficient academic infrastructure, more committed and qualified teachers, and acquire quality education resources. Although some societies have taken measures such as sponsoring children and providing free education to encourage parents to take their school-going children to school, the link between poverty and lack of education is likely to continue being a societal problem because illiteracy negatively impacts a society’s economic growth leading to more poverty and related issues such as crime.
Proposed Solutions
The impact of poverty on education can be mitigated through government and community involvement. According to UNICEF (2020), the government should focus on funding learning institutions where children from low-income families are most represented by prioritizing allocating public funding to institutions in low-income neighborhoods and gradually increasing funding to higher education levels with a continued focus on the most vulnerable and children living in extreme poverty. The community should advocate for equity in the education sector to guarantee that the needs of children living in poverty are met. The community should also participate in generating evidence and data better to understand the needs of children from low-income families.
The impact of poverty on education can also be addressed through education reform. According to Ewiss (2020), education restructuring in developing nations represents many children’s real investment in acquiring reading, writing, critical thinking, and numeracy skills, reducing the spread of disease, poverty, and ignorance. The author argues that low-income families should be encouraged and supported to enroll their children in learning institutions for the reform plans to succeed while reducing the cost of education and caring for teachers professionally and financially. Ewiss (2020) argues that developing countries should develop diversified and solid education strategies and policies and supervise their implementation. Governments are responsible for creating these policies by actively implementing compulsory and free education and preventing school dropouts. The most effective way to prevent school dropouts is by collaborating with teachers and the community to identify the causes of the dropouts and effective measures to retain students in schools.
Statistical Data
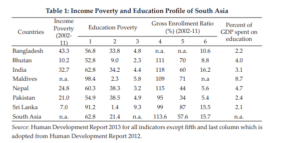
Over the past decade, the significance of education in society has spurred debate, especially because of the vital role of education in developing communities and driving innovation. Various researchers have explored the relationship between poverty and lack of education in different parts of the world. A study conducted by Thapa (2015) in South Asia found that by 2011, half of the population of illiterate people in the world lived in South Asia. The study also found that the adult literacy rate in South Asia is more than 40%. However, poverty is the leading cause of illiteracy in the region, as indicated in Table 1 below.
(https://www.nepjol.info/index.php/EJDI/article/view/11873)
Based on the data presented in the table above, a negative relationship exists between adult illiteracy and poverty in South Asia because a decrease in income poverty leads to an increase in adult literacy. Another study conducted by Nadeem et al. (2021) found that 38% of the people living in Pakistan live below the poverty line and cannot manage education costs, leading to high illiteracy in the region. According to Lindor (2019), most people in developing countries cannot write or read because they must constantly work to support their families and are sometimes victims of labor exploitation. The authors also argue that poverty may lead to a lack of education because of the stress faced by students from poor backgrounds, the lack of financial resources needed to meet education costs, and the deterioration of the standards of education provided in schools in low-income neighborhoods.
The article by Thapa (2015) is valid because it is published in a valid journal. The author also uses statistical data from different regions to test the research hypothesis and provide accurate information. The article is reliable because the author supports his findings with findings from past similar studies. The article by Nadeem et al. (2021) is valid because the author uses past findings to support his arguments. The article has also been published in a reliable journal, thus enhancing its validity. The article is reliable because data from peer-reviewed articles and books support all arguments. The article is also reliable because it was accepted by the Department of Education at the Islamia University of Bahawalpur in Pakistan. The article by Lindor (2019) is valuable because it has been licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International. The article is reliable because it contains data from past journal articles, books, and reports prepared by non-governmental organizations such as UNESCO and ECLAC. The three articles do not contain any biases, thus enhancing the accuracy of the information shared with the target audience. One of the strengths of the three sources is the use of findings from other research studies to support the arguments made by the authors. The second strength is the effective transitioning from one section to another, making it easier for the reader to follow through and get the information they seek. The third strength is a strong thesis statement indicating the article’s discussion. The main weakness in the three articles is the use of outdated peer-reviewed articles. Nadeem et al. (2021) and Thapa (2015) articles also lack a detailed discussion of the research findings.
The main limitation of the current research is limited recent data on the relationship between poverty and lack of education. Most of the existing research on the impact of poverty on education was conducted more than ten years ago, thus limiting the relevance of the information in modern societies. The second limitation is time constraints. There was limited time to go through all the relevant peer-reviewed articles and books to get the information related to the current research’s thesis statement because of the assignment deadlines and course requirements, which could impact the amount of information analyzed and shared in the research. The topic being studied in the current research was also too broad, hence the need for future research to break it down into different sections, such as the impact of poverty on willingness to join a school, the impact of poverty on school dropouts, and the impact of poverty on education affordability.
Ethical Issues Related To The Proposed Solutions
The effectiveness of the proposed solutions requires addressing ethical issues that could emerge in the implementation process and the ethical outcomes of the decisions linked to each solution. The positive ethical outcome that could result from government and community involvement is respect for legal, human, and civil rights. Every individual has the right to education so that they can acquire knowledge, skills, and competencies that they can use to improve their lives. Government and community involvement in ensuring that child-going children go to school upholds this right, thus creating a positive ethical outcome. However, the solution could also have a negative ethical outcome by interfering with people’s ability to participate in determining what they need and want. For instance, a child may be forced to go to school against their will because the government and community believe education is best for them. Parents may also have limited control over the decision to take their children to school, especially if they struggle to afford school fees, thus creating ethical issues. The negative ethical outcome can be mitigated by doing what is best for the child and the parents and explaining to parents the importance of education.
The positive ethical outcome that could result from education reform is creating equality in education access for children from poor backgrounds. Education reforms may focus on increasing the affordability of basic education and ensuring that all learning institutions, including those in poor neighborhoods, have trained teachers so that all children can access quality education. Conflict of interest could be The negative ethical outcome of this solution. Policymakers in charge of making reforms may have conflicts of interest when they want to protect their needs, leading to unfair reforms that disadvantage some students and parents. For example, education reforms may require school-going children to purchase books and always wear school uniforms to benefit the individuals distributing school uniforms and books despite knowing that some low-income families may not be able to afford to pay those expenses. The negative ethical outcome can be mitigated by engaging all stakeholders in making decisions about proposed education reforms.
Conclusion
Lack of education is a serious issue that contributes to slow development in the affected societies, hence the need to actively engage the community members, parents and guardians, and local leaders in policymaking and education reforms to ensure that all children in the community acquire basic education. The impact of poverty on the lack of education is evident in developing countries, where most families struggle to afford school fees and opt to engage their children in looking for income to sustain the family. The impact of poverty on education is also evident in some developed countries such as Canada, where poverty is linked to poor academic achievement caused by limited parental education and family stress. Statistical data from different countries in South Asia also indicates that poverty causes a lack of education. The two solutions that can be used to reduce the impact of poverty on education are community and government involvement and education reform. Although community and government involvement promotes equality, it denies parents and children the freedom to choose what they want. Consequently, education reform promotes equality but could be impacted by conflicts of interest. It is, therefore, important to constantly monitor the implementation of these solutions to address any issues that could impact their effectiveness.
References
Bhargava, V. K. (2006). Global issues for global citizens: An introduction to key development challenges. World Bank Publications.
Ewiss, M. A. (2020). Issues in Education Development in Developing Countries. IOSR Journal of Humanities And Social Science (IOSR-JHSS), 25(11), 64-75.
Ferguson, H., Bovaird, S., & Mueller, M. (2007). The impact of poverty on educational outcomes for children. Paediatrics & Child Health, 12(8), 701–706. https://doi.org/10.1093/pch/12.8.701
Lindor, M. (2019). Public policies, poverty and illiteracy in young and adults in Haiti. Challenges and perspectives. Revista Interamericana de Educación de Adultos, 41(1).
Mihai, M., Ţiţan, E., & Manea, D. (2015). Education and poverty. Procedia Economics and Finance, 32, 855-860. https://doi.org/10.1016/s2212-5671(15)01532-4
Nadeem, T., Akhtar, N., & Ahmad, M. (2021). A study of the relationship between family income and literacy level. Statistics, Computing And Interdisciplinary Research, 3(2), 59–69. https://doi.org/10.52700/scir.v3i2.50
Thapa, S. B. (2015). Relationship between education and poverty in Nepal. Economic Journal of Development Issues, 148–161. https://doi.org/10.3126/ejdi.v15i1-2.11873
UNICEF. (2020). Addressing the learning crisis: An urgent need to better finance education for the poorest children. https://www.unicef.org/media/63896/file/Addressing-the-learning-crisis-advocacy-brief-2020.pdf
ORDER A PLAGIARISM-FREE PAPER HERE
We’ll write everything from scratch
Question
Write this final paper, an argumentative essay that will present research relating critical thinkers to the modern, globalized world. In this assignment, you need to address the items below in separate sections with new headings for each.

Global Lack of Education
In your paper,
Identify the global societal problem within the introductory paragraph.
Conclude with a thesis statement that states your proposed solutions to the problem. (For guidance on how to construct a good introduction paragraph, please review the Introductions & Conclusions. Links to an external site. From the University of Arizona Global Campus Writing Center to an external site..)
Describe background information on how that problem developed or came into existence.
Show why this is a societal problem.
Provide perspectives from multiple disciplines or populations so that you fully represent what different parts of society have to say about this issue.
Construct an argument supporting your proposed solutions, considering multiple disciplines or populations so that your solution shows that multiple parts of society will benefit from this solution.
Provide evidence from multiple scholarly sources indicating your proposed solution is viable.
Interpret statistical data from at least three peer-reviewed scholarly sources within your argument.
Discuss the validity, reliability, and any biases.
Identify the strengths and weaknesses of these sources, pointing out limitations of current research and attempting to indicate areas for future research. (You may even use visual representations such as graphs or charts to explain statistics from sources.)
Evaluate the ethical outcomes that result from your solution.
Provide at least one positive ethical outcome as well as at least one negative ethical outcome that could result from your solution.
Explain at least two ethical issues related to each of those outcomes. (It is important to consider all of society.)
Develop a conclusion for the last paragraphs of the essay, starting with rephrasing your thesis statement and then presenting the topic’s major points and how they support your argument. (For guidance on how to write a good conclusion paragraph, please review the Introductions & Conclusions. Links to an external site. From the University of Arizona Global Campus Writing Center to an external site..)