Falls among Older Patients in Long Term Care Facilities
Abstract
Falls are a major health concern. They result in significant suffering and morbidity to the affected persons. Falls incidents in long-term care facilities are often challenging to caregivers. The quality improvement plan focuses on fall prevention. The Fall TIPS toolkit is an effective quality improvement plan against falls: Falls among Older Patients in Long Term Care Facilities.
It is thus important that the program is implemented across long-term care facilities. Implementation of the Fall TIPS programs draws interdisciplinary teams and can be evaluated using the PDCA model. The program aligns with the federal benchmarks outlined by AHQR and will be successful in case there is a reduction in the fall rates.
Keywords: falls, fall rates, Fall TIPS toolkit, long-term care facilities
Falls among Older Patients in Long Term Care Facilities
Falls remain a major health concern. Whenever they occur, they result in injuries, significant suffering, and functional decline in the affected persons. Falls incidents in long-term care facilities are often challenging to the caregivers.
They have been linked to higher rates of morbidity and death and pose a serious threat to the safety and quality measures in these facilities (Guirguis-Blake et al., 2024). This warrants their address. Fall prevention remains a priority when caring for older adults. This paper details a quality improvement plan for falls in long-term care facilities.
Quality Improvement
Quality Improvement Initiative
Quality improvement in falls management focuses on preventing falls. Fall prevention programs, such as the Fall TIPS toolkit, are one of the initiatives that are effective in mitigating falls. Fall TIPS is a novel patient-centered initiative that is effective in reducing fall rates among older adults.
It reduces adult fall rates in inpatient care settings (Dykes et al., 2020). It can, therefore, be applied to residents of long-term care facilities to lower their risk of falling.
Quality Improvement Plan
A quality plan utilizing the Fall TIPS toolkit is geared towards enhancing caregivers’ capacity to handle patients’ falls. It encompasses educating healthcare providers in handling older adults about Fall TIPS and integrating the tool into the routine operationalization of the facilities. This is expected to enhance caregivers’ accountability when managing those at risk of falling and subsequently reduce the fall rates.
Goals and Outcomes
The quality improvement initiative and plan provide a pathway toward reducing falls within long-term care facilities. The first goal is to enhance providers’ knowledge of Fall TIPS before its implementation. This will improve its adoption and effectiveness in lowering fall rates (Lee et al., 2024). The second goal is to educate the patient on Fall TIPS within the first week of program implementation to enhance their understanding of the personal fall risks and measures to curtail falls.
The third goal is to reduce fall rates by 30% within two months of full implementation of the program. The program is expected to reduce fall rates within long-term care facilities. Likewise, healthcare providers involved in handling long-term care facilities residents and the residents should maintain knowledge of diverse aspects of falls, such as risk factors and prevention interventions.
Shareholders Involved and Responsibilities
The quality improvement plan will draw diverse shareholders. These include healthcare providers involved in handling long-term care residents, such as nurses, physicians, healthcare administrators, and patients. Healthcare providers are the actual implementors of the plan. They play a role in integrating the Fall TIPS program into their normative fall prevention activities.
In this respect, they educate the patients on the perceived fall risks and measures to curtail them. Likewise, they collaborate in identifying fall risks and the specific patient-centered interventions to mitigate them. Healthcare administrators provide the necessary funds required for the project.
They also guide the change process necessary to implement the program and influence healthcare professionals to adopt it. Residents of the long-term care facilities are the subjects of the plan. They play a role in participating in the educative program targeted at enhancing their capacity toward fall prevention.
How Interprofessional Collaboration Impacts the Project
The program is heavily dependent on interprofessional collaboration. It helps in bringing together healthcare professionals from different cadres to assess patients’ fall risks and develop a patient-specific plan on how to curtail them. It also ensures the effective implementation of fall prevention interventions, ensuring an overall reduction in fall rates.
Quality Model
The development, implementation, and evaluation of the project will utilize the plan-do-check-act (PDCA) model. The model postulates a four-step approach to implementing healthcare interventions. In the plan phase, program goals will be outlined. In this case, the goal is to reduce fall rates in long-term care facilities.
In the do phase, the plan is actualized. Here, the fall TIPS toolkit will be implemented in longer-term care facilities. In the analysis phase, the program will be evaluated to ascertain whether it met its goals. Any identified improvement areas will then be implemented in the act phase.
Types of Measures
The proposed quality improvement plan will be evaluated against its objectives. In this respect, fall rates will be measured to ascertain whether the program resulted in a meaningful reduction in the number of reported falls. The dependent variables in this case are fall rates and participants’ understanding of the Fall TIP tool. These will be measured to determine whether the program was successful.
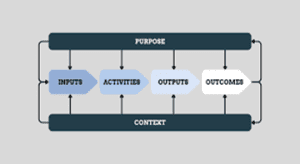
Diagram of the Logic Model
Kinds of Reliability and Validity
Reliability defines the consistency of a measurement. The inter-rater reliability scale is the kind of reliability that will be used to evaluate the program’s measurements.
Inter-rater reliability details the level of congruence between observers evaluating the same item. Likewise, construct validity will be used to evaluate the program. Construct validity is based on how well the measure matches the intended concept.
Benchmarks
The program utilizes the benchmarks on quality improvement in fall prevention outlined by the Healthy People 2030 initiative and the Agency for Healthcare Quality and Research. These benchmarks highlight why fall prevention is important and the role of caregivers in mitigating falls (Turner et al., 2020). The benchmarks are aligned with the provision of the program. Both are geared towards reducing fall rates among older adults.
Actions and Timeframes
The program will follow a three-step approach that starts with a patient assessment to determine their fall risk status. This step is expected to last two to three hours and draw an interdisciplinary team. A Fall TIPS toolkit will then be developed. The toolkit will be tailored to the identified risks.
This step is also expected to last 2 to 3 hours. The final stage is to implement the plan. This will include patient and caregiver education on the tool and subsequent use.
This step is expected to last between three to four weeks. The plan fits into the strategic plan as it meets the timelines. It can also be performed where resources are limited.
In conclusion, falls remain a major health concern. They result in significant suffering and morbidity to the affected persons. The Fall TIPS toolkit is an effective quality improvement plan against falls.
It is thus important that the program is implemented across long-term care facilities. Implementation of the Fall TIPS programs draws interdisciplinary teams. The program is successful in case there is a reduction in the fall rates.
References
Dykes, P. C., Burns, Z., Adelman, J., Benneyan, J., Bogaisky, M., Carter, E., Ergai, A., Lindros, M. E., Lipsitz, S. R.,
Guirguis-Blake, J. M., Perdue, L. A., Coppola, E. L., & Bean, S. I. (2024). Interventions to prevent falls in older adults. JAMA, 332(1), 58. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2024.4166
Lee, H.-C., Hsieh, C.-J., & Jerng, J.-S. (2024). Incidence and factors associated with falls in older people in a long-term care facility: A prospective study in Taiwan. Healthcare, 12(10), 959. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare12100959
Turner, K., Staggs, V. S., Potter, C., Cramer, E., Shorr, R. I., & Mion, L. C. (2020). Fall prevention practices and implementation strategies: Examining consistency across hospital units. Journal of Patient Safety, 18(1). https://doi.org/10.1097/pts.0000000000000758
ORDER A PLAGIARISM-FREE PAPER HERE
We’ll write everything from scratch
Question
Module 4: Scholarly Paper
Assignments this week are related to the following course outcomes:
- Assess outcome data, gaps in data, patient safety data, quality management systems, and economic outcomes to compare with national benchmarks relevant to quality improvement in health care systems (CSLO1). Evaluate a variety of quality improvement and evidence based practice models for quality improvement and risk assessment quality outcomes (CSLO3).
Scholarly Paper Guidelines: Develop a quality improvement plan. Review quality improvement initiatives and quality and logic models utilized by outcome evaluation agencies such as QSEN, AHRQ or JC.
Template for paper
Here is a template to assist you with writing a good scholarly paper.
- APA Template 7th ed DNP Program.docx
Falls among Older Patients in Long Term Care Facilities
Lecture Materials:
- Levin & Lauder, Ch 8 & Ch 10
- Assigned reading
- Articles: (Please follow this link to access some of the articles listed)
- This article discusses evidence-based practice models: DNP 805 Evidence_based_models.pdf
- This article is an overview of a Logic Model Framework: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3266837/ (Links to an external site.)Links to an external site.Links to an external site.
- This article is about safety and quality in curricula: DNP 805 Quality and Safety Curricula (1).pdf
- This article discusses healthcare and teamwork: DNP 805 TeamSTEPPS (1).pdf
- This article discusses the value of quality and safety teams: DNP 805 Value of Quality and Safety Teams.pdf
- Articles: (Please follow this link to access some of the articles listed)
- Extra Learning Materials:
- This is an example of a root cause analysis: DNP 805 RCA Blank Template example.doc
Note:
- Select a topic