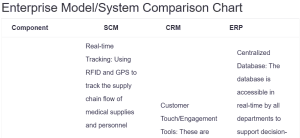
Enterprise Model/System Comparison Chart
| Component | SCM | CRM | ERP |
| Elements of System: Define the elements of the system (e.g., capabilities, major features, effects on business operations). | Real-time Tracking: Using RFID and GPS to track the supply chain flow of medical supplies and personnel
Inventory Management: The platform has ensured availability and reduced shortage/wastage of extremely critical medical supplies and vaccines.
Coordination Tools: The system will help communicate appropriately between emergency responders, hospitals, and public health agencies for smoother functioning of resource allocation.
|
Customer Touch/Engagement Tools: These are the tools that allow communication between the public and the stakeholders in the incident.
Feedback Mechanisms: The mechanism of gathering information from the community for response operations.
Data Analytics: Analytics for assessing public sentiment and demands related to a bioterrorism incident.
|
Centralized Database: The database is accessible in real-time by all departments to support decision-making.
Financial Management Tools: The financial management tools help manage budgets related to emergency response effectively.
Human Resources Integration: Human resources integration enables smooth personnel management for quick deployment during emergencies (Edvardsson & Durst, 2021).
|
| Benefits to Business: Describe the system’s benefits to the business (e.g., internal processes, external impact on customers, suppliers, delivery channels, other stakeholders). | Efficient Resource Allocation: A crisis would demand better distribution of medical supplies to ensure timely delivery at the point of need.
Reduced Response Times: Reduces the time it takes for the facilitation of essential resources to the affected areas and could save lives in the process.
Better Partnerships: Promotes collaboration among all stakeholders in the provision of a unified response to every emergency or disaster.
|
Improved Community Relations: Proactive engagement builds trust among the citizens.
Better Credibility in Crisis Situations: Transparency in communication increases public trust in times of crisis.
More Responsiveness: Timely response to queries leads to better public perception.
|
Smooth Operations: The system integrates different functions, reducing duplication of work and enhancing efficiency during an emergency.
Data Accuracy: A centralized database eliminates manual entry errors at the departmental level (Wisdom et al., 2022).
Interdepartmental Coordination: It coordinates teamwork since it offers a single platform for information sharing. |
| Cost (H/M/L): List your high-level cost estimate (high/medium/low) of the system implementation. | Implementation Costs: Initial investment in SCM software and technologies may be expensive.
Training of Personnel: Training is a continuous process needed to retain the knowledge of using SCM tools among the staff.
Maintenance and Updates: Periodic updates are needed on software and systems, which is necessary for their use and security.
|
Software Costs: The investment in CRM software solutions is high.
Training Costs: Employees need to be trained about the usage of CRM, which again involves costs.
Integration Costs: Integrating the CRM with the prevailing system also requires additional resources.
|
High Initial Investment: Most of ERP systems require lots of initial investments in purchasing software and hardware.
Maintenance Costs: The processes require periodic updating and maintenance to perform well. Training and Support Costs: ERP systems require constant training and development to ensure the staff are informed on how to use such systems (Jo & Park, 2023).
|
| Impact on Competitive Advantage (H/M/L): Estimate (high/medium/low) the system’s impact on ABC Company’s competitive advantage and position in the market. | Reputation Building: Quick and efficient response develops a good public reputation.
Differentiation: The company differentiates itself from various organizations, as some of them cannot handle logistics even in crises.
|
Building Loyalty: Good relationships create community loyalty, which is crucial in emergencies.
Reputation Management: Accomplished through more effective dissemination of information to reduce adverse impressions resulting from emergencies.
|
Benefits of Operational Efficiency: As efficiency increases, it creates more room for cost savings, which then can be used in other areas of the organization.
Competitive Advantage: Speed enhances response times in the event of an emergency, resulting in better service and improved competitive advantage.
|
| Integration Difficulties (H/M/L): Estimate (high/medium/low) any difficulties ABC Company will likely encounter integrating this system into its existing processes and legacy systems with which it will interact. | Stakeholder Alignment: To align the interests of all the stakeholders in the value chain.
Data Sharing: Sharing real-time data between suppliers and buyers requires a sound IT infrastructure and trust between the partners.
|
Alignment with existing communication platforms: Integration of CRM with the current platform in some instances may involve adjustments in the current operations.
Data Integrity: Several platforms are bound to present challenges to ensure that correct data and proper engagement is achieved.
|
Complicated Implementation: The implementation of the ERP systems in the other departments may be tricky due to differences in process and culture.
Employee Resistance to Change: Employees may resist taking on new systems, thus affecting the successful implementation of such systems.
|
| ROI (H/M/L): Estimate (high/medium/low) the financial return on investment (ROI) ABC Company can expect from this system.
Use the following formula to guide your estimate: ROI % = [(new incremental revenue + cost savings to the business) − cost of the investment] ∕ cost of the investment × 100. |
Cost Reduction: The reduction in operational costs can be significant while dealing with any emergency with the help of an integrated supply chain operation.
Long-term Benefits: Building public trust through crisis management will provide support from the community in the future.
|
Improved Engagement: More engagement by the public results in a better flow of information and adherence to health measures during an emergency.
Long-term Loyalty Benefits: Positive experiences due to an emergency will result in long-term relationships and loyalty gain in the community.
|
Long-term Cost Savings: Efficient operations ensure that, over time, operational costs are reduced.
Decision-Making Improved: It would be easy to make prudent strategic decisions at the actual time of crisis with access to data in real-time.
|
References
Edvardsson, I. R., & Durst, S. (2021). Human resource management in crisis situations: A systematic literature review. Sustainability, 13(22), 12406. https://doi.org/10.3390/su132212406
Jo, H., & Park, D. (2023). Mechanisms for successful management of Enterprise resource planning from user information processing and system quality perspective. Scientific Reports, 13(1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-39787-y
Wisdom, A., Isaac, U., & Philibus, A. (2022). An Optimized Database Management System [Paper presentation]. Proceedings of the LASUSTECH 30th iSTEAMS Multidisciplinary Innovations Conference.
ORDER A PLAGIARISM-FREE PAPER HERE
We’ll write everything from scratch
Question
The purpose of this chart is to gather and compare information about three different models/systems. You will complete the chart in stages as your Weeks 3, 4, and 5 assignments. In the chart, the Component column explains the information requested. Enter the information in the appropriate column for that week’s assignment. Ensure you address all prompts and information requested.
- For Week 3, complete the SCM column of the chart.
- For Week 4, complete the CRM column of the chart.
- For Week 5, complete the ERP column of the chart.
Enterprise Model/System Comparison Chart
| Component | SCM | CRM | ERP |
| Elements of System: Define the elements of the system (e.g., capabilities, major features, effects on business operations). | |||
| Benefits to Business: Describe the system’s benefits to the business (e.g., internal processes, external impact on customers, suppliers, delivery channels, other stakeholders). | This is especially important as an ERP model/system should have a major impact on standardizing internal processes across all business functions, thereby reducing costs and increasing productivity. | ||
| Cost (H/M/L): List your high-level cost estimate (high/medium/low) of the system implementation. | |||
| Impact on Competitive Advantage (H/M/L): Estimate (high/medium/low) the system’s impact on ABC Company’s competitive advantage and position in the market. | This is especially important as a CRM system should have a major impact on attracting new customers and retaining existing ones. | ||
| Integration Difficulties (H/M/L): Estimate (high/medium/low) any difficulties ABC Company will likely encounter integrating this system into its existing processes and legacy systems with which it will interact. | As the ERP standardizes company processes, this should be an area of focus during implementation of this model/system. | ||
| ROI (H/M/L): Estimate (high/medium/low) the financial return on investment (ROI) ABC Company can expect from this system.
Use the following formula to guide your estimate: ROI % = [(new incremental revenue + cost savings to the business) − cost of the investment] ∕ cost of the investment × 100. |
Pay special attention to cost savings that should be expected from the use of an SCM model/system (e.g., better supply forecasting, inventory management, delivery logistics).
|
Pay special attention to new incremental revenue that should be expected from the use of a customer-facing CRM model/system (e.g., better customer acquisition, retention, repeat business).
|
Pay special attention to cost savings that should be expected from the use of an ERP model/system (e.g., consistent internal processes, increased productivity, efficiency improvements).
|