Discussion – Virtualization
Virtualization is a technique that enables the separation, extension, or replacement of an existing interface into several fully independent virtual interfaces to emulate the behavior of a real system/interface. It is also known as the technique that embodies the virtual interface from the physical supply of the interface (resource request or application). New virtual interfaces provide a similar experience to the real interface of the device. A software part that abstracts various virtual machines/interfaces operating on the same device is known as the hypervisor (3).
Need of Virtualization in an Organization
Virtualization has been around for several decades, even though most virtualization technologies have yet to become mainstream. In recent years, a growing number of companies have begun recognizing and appreciating the benefits associated with virtualization (4). Some of the benefits virtualization has availed to organizations include:
- Improvement of Disaster Recovery Efforts.
Disaster recovery is based on the ability to recover files after a disaster. It’s easier to back up a fully virtualized infrastructure by copying VM file images compared to backing up separate hardware servers.
- Increase in Business Continuity.
Business continuity is an essential aspect of any organization. A good business continuity plan ensures that business operations are disrupted to a minimal or zero level in the event of a disaster. With server hardware failure being the most common cause of failure in a data center, virtualization functions such as live migration on a server help maintain business continuity by eliminating downtime.
- Increase in Server Efficiency.
Server-side virtualization is intended to use computing power more effectively in relation to processor cycles and RAM. In addition to energy management and lower cooling costs, with virtualization, small and medium-sized companies are able to minimize capital costs by purchasing fewer physical servers to replace a greater number of outdated equipment when it is shut down.
Virtual Technologies/Solutions.
-
Full Virtualization.
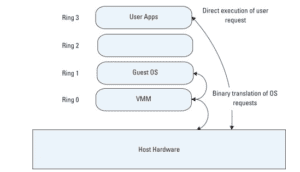
This technique is used to provide a Virtual Machine Environment (VME) that simulates the underlying hardware in a complete manner. Every software that can be executed on physical hardware can be executed in this type of environment in the VM, and every operating system supported by the underlying hardware can be operated on each VM. Users will concurrently run several separate guest OSes. The VM simulates enough hardware in full virtualization to allow an unmodified guest OS to run in isolation. In a variety of cases, this is particularly helpful. Experimental new code can, for instance, be run in OS innovations in a separate Virtual Machine (VM) along with older versions (1). The hypervisor offers all the physical machine resources, including virtual BIOS, virtual devices, and virtual memory management, to each VM. The Guest OS is completely deactivated by the virtualization layer from the underlying hardware.
Fig 1: Full Virtualization.
-
Paravirtualization.
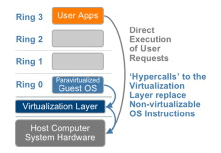
Paravirtualization requires the OS kernel update. The OS kernel serves as a link between applications and hardware processing. Paravirtualization substitutes hypercalls for non-virtualizable directions interacting directly with the hypervisor of the virtualization layer. The definition of a hypercall is the same as that of a machine call. The program uses system calls to request resources from the OS and provides an interface between the request or method and the OS. Apart from the hypervisor, hypercalls function the same way (1). The hypervisor also offers hypercall interfaces for other kernel tasks, such as control of storage and managing interrupts.
Fig 2. ParaVirtualization.
Virtualization Alternatives.
-
Containerization
Containerization is a type of virtualization of the operating system in which applications are managed in isolated user areas known as containers using the same standard Operating System (OS). An effectively complete packaged and portable computer environment is a container:
- The framework has encapsulation and isolation into its container anything required for the execution – its binaries, libraries, configuration files, and dependencies.
- The container is disconnected from the host OS with minimal access to basic resources, just like a lightweight virtual machine (VM).
- The containerized application can, therefore, be running with a number of different infrastructure forms — bare metal, VMs, and cloud — without having to refactor for any environment.
-
Hypervisor
A hypervisor is software that connects hardware and virtual machines (VM) and acts as a resource broker (5). The hypervisor generates and runs virtual machines and may also be known as a virtual monitor. A hypervisor can accommodate multiple guest VMs on one host machine by digitally sharing resources, including memory and processing. Since guest VMs are independent of host hardware, hypervisors allow the use of greater resources and greater IT mobility of a device. This makes switching between different servers simple since a hypervisor can run several virtual machines on one physical server:
Security Risks of Virtualization.
There are a number of possible malicious acts or threats that may breach the security constraints of computer systems (2). Security risks associated with virtualization include:
Unauthorized Disclosure
This is Unauthorized access to confidential information. This can be obtained by an intruder who bypasses the safety requirements of the framework.
To avoid this, access control is used to enable a framework to control which organizations may access their functions and which permissions each of them has. Entities must be correctly authenticated in the framework to grant individual access rights and permissions.
Deception.
This threat involves an intentional attempt to mislead other entities by sending incorrect or misleading information. The countermeasure for deception is Authentication, which ensures that all interacting entities are actually the entities they claim to be. The recipient of a message must be able to identify its transmitter correctly, and an object must not be able to transmit an alternative.
Disruption.
This is a class of threats that cause devices to malfunction or degrade, impacting the services provided by the organization.
Disruption can be avoided by introducing Data Confidentiality, which ensures that third parties are not provided with access to sensitive information between two organizations. The system should also inhibit attackers by evaluating traffic flow features from deriving information.
Usurpation.
This involves unauthorized control, allowing an attacker to illegitimately access or exploit the device itself to trigger incorrect or malicious behavior.
To counteract this threat, data integrity is introduced into the system, ensuring that data is not manipulated, adulterated, or destructed by individuals or distributed through a network. In addition, data corruption recovery mechanisms may also be developed to guard against unauthorized control.
Sources
Barrett, D. (2010). How Virtualization Happens. Virtualization and Forensics.
Bays, L.R, & Barcellos, M.P. et al. (2015). Virtual network security: threats, countermeasures, and challenges. Journal of Internet Services and Applications. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13174-014-0015-z
Gursimran Singh, & Gurjit Singh Bhathal. (2006). An Overview Of Virtualization. INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF COMPUTERS & TECHNOLOGY, 5(3), 167-171. https://doi.org/10.24297/ijct.v5i3.3518
Ivan Pogarcic, & David Krnjak. (2012). Business Benefits from the Virtualization of an ICT Infrastructure. International Journal of Engineering Business Management, 4(1), 1. doi:10.5772/51603
Stallings, W. (2019). Effective CyberSecurity. New York: Pearson Education, Inc
ORDER A PLAGIARISM-FREE PAPER HERE
We’ll write everything from scratch
Question

Discussion – Virtualization
Virtualization offers organizations these benefits:
Savings on infrastructure and support costs.
Fast recovery of information systems in the event of an equipment mishap.
New opportunities for disaster recovery and business continuity.
In addition to examining these virtualization benefits in this assignment, you will also examine challenges associated with virtualization. Specifically, you will write a 2–3-page paper in which you:
Define virtualization.
Justify the need for organizations to use virtualization.
Evaluate two virtual technologies/solutions.
Determine alternatives to virtualization.
Research security risks associated with virtualization and potential countermeasures.
Go to Basic Search: Strayer University Online Library to locate and integrate into the assignment at least three quality, peer-reviewed academic resources written within the past five years.
Include your textbook as one of your resources.
Wikipedia and similar Websites do not qualify as quality resources.