Conditioned Reinforcer and Conditioned Aversive Stimulus
Part 1: Setting the Scene
Conditioned Reinforcer
In Daniel’s class, the teacher can use a process known as “pairing” to create conditioned reinforcers. Pairing involves associating an unconditioned reinforcer or punisher with a neutral stimulus to strengthen the subject’s response when presented with the neutral stimulus again (Malott, 2015, p. 215). It also involves repeating the process several times until the neutral stimulus takes on a reinforcing or punishing quality. In Daniel’s class, the teacher can pair tokens (the neutral stimulus) with the prize box (the conditioned reinforcer). The neutral stimulus here is the token board, and the unconditioned reinforcer is the prize box or item in the prize box that Daniel is working to receive.
On the first day, the teacher can place a token on the board and then point to the prize box as a reward for working. The teacher gives instructions and then presents the token board. If Daniel then chooses to work, he earns a token and can exchange it for an item in the prize box. On the second day, the teacher does the same thing and repeats this process for several days. Eventually, Daniel starts associating tokens with his work and the prize box. This creates a conditioned reinforcer; when he sees the token board, it motivates him to complete his work to get access to the prized item. In this example, the conditioned reinforcer is the prize box or item in the prize box that Daniel is working for. The neutral stimulus has been associated with the conditioned reinforcer through pairing and repetition, and now it acts as a motivator to get Daniel to work. This example demonstrates how classical conditioning can be used to improve learners’ productivity effectively.
Conditioned Aversive Stimulus
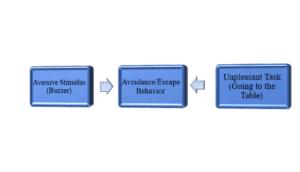
The teacher can also use pairing to create a conditioned aversive stimulus. Aversive stimulus refers to an unpleasant stimulus that causes a decrease in behavior. This can be done by repeatedly presenting a neutral stimulus (such as work tasks) with an unlearned punisher (like a scolding). In Daniel’s case, the teacher can pair an unpleasant sound, such as a buzzer, with the task of getting up to go to the table (Malott, 2015, p. 227). The sound can irritate, distract, and discourage Daniel from getting up to do his work. A neutral stimulus, such as getting up to the table, is then associated with an aversive stimulus (like the buzzer), which leads to escape-maintained behavior.
On the first day, when Daniel is expected to go to the table for work, he will be presented with an unpleasant sound (buzzer) when he gets up. At first, it discourages him from going to the table, but Daniel may still choose to go (Gentilini & Greer, 2020). On the second day, the same unpleasant sound will be present, but this time, he may choose to avoid it altogether, leading to escape-maintained behavior. The teacher can increase the frequency by pairing the neutral stimulus (getting up to the table) and aversive stimulus (buzzer) multiple times until Daniel associates getting up with unpleasantness, thus avoiding it altogether. It can be every 5 minutes or 15 minutes, depending on how quickly the teacher wants to see the desired behavior. Every time Daniel gets up and goes to the table, he will be presented with an unpleasant sound, which will eventually lead him to avoid going to the table in order to escape the aversive stimulus (buzzer). The decreasing rate of behavior (getting up and going to the table) is an example of escape-maintained behavior. Sometimes, escape-maintained behavior is also referred to as negative reinforcement.
Diagram of Punishment Contingency
PS360: Unit 4 Diagram Worksheet
References
Gentilini, L. M., & Greer, R. D. (2020). Establishment of conditioned reinforcement for reading content and effects on reading achievement for early-elementary students. The Psychological Record, 70(2), 327-346.
Malott, R. (2015). Principles of behavior. Psychology Press.
ORDER A PLAGIARISM-FREE PAPER HERE
We’ll write everything from scratch
Question
You have learned that some many unlearned reinforcers and punishers impact behavior, such as food, water, warmth, etc. You know that behavior that gains access to such reinforcers tends to repeat. But there are behaviors that we engage in every day that are not reinforced or punished by these unlearned stimuli. In Unit 4, you have learned how neutral stimuli can be conditioned to influence behavior. Through pairing with unlearned reinforcers (or punishers) or previously conditioned reinforcers or punishers, neutral stimuli can be transformed into conditioned reinforcers or punishers to maintain or diminish behavior effectively.

Conditioned Reinforcer and Conditioned Aversive Stimulus
Watch the Unit 4 Lecture. (click here for transcripts)
Read the following scenario.
Part 1: Setting the Scene
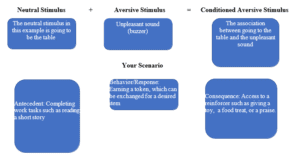
Every time Daniel is presented with a work task, he cries. Usually, work is done at the table, and now, Daniel doesn’t even want to sit at the table for lunch. This has become a problem, and now the teacher doesn’t know where to start. He knows that when he completes his work, he will earn a token on his token board and exchange it for an item in the prize box. Eventually, he will complete part of his work on the floor and earn his tokens.
Conditioned Reinforcer: Explain how “pairing” can create conditioned reinforcers (learned reinforcers). Use the scenario in Daniel’s class to illustrate the process of pairing. What is the conditioned reinforcer in this example?
Conditioned Aversive Stimulus: From the above scenario, explain how a neutral stimulus was transformed into a conditioned punisher (learned aversive stimulus) through the process of pairing and how this can evolve into escape-maintained behavior.
Diagram the above punishment contingency. (Hint: The contingency should be an escape or punishment).
Part 2: Complete the Discussion Question Worksheet
Complete the worksheet based on this week’s primary discussion post. Attach your finalized worksheet as part of your final primary post.
Conditioning an Aversive Stimulus Worksheet