Comprehensive Summary of a Quality Improvement Project- From Practicum to Implementation
Hello, and welcome to my QI project presentation, which summarizes the elements of the entire QI project, from practicum hours and practicum settings to the point of the project’s implementation.
The practicum hours introduce the student nurse to practical settings in which they get an opportunity to apply what they have learned in the classroom in real-life practice settings. This presentation will cover the practice settings where my practicum hours will be covered, the healthcare issue of interest during my practicum hours, and the problem identified in the practice settings that require a QI project. It will also cover the proposed QI project, the developed PICO(T) question and search strategy, the reviewed literature, and the selected theory/model to support implementation, as well as the proposed implementation and measurement plan.
The practicum hours will take place within the primary care settings. I am required to cover a total practicum of 30 hours. Throughout the practicum hours, the focus will be majorly on managing pediatric patients. A clinical concern of interest during practicum hours that is notable among the pediatric populations is juvenile diabetes or Type 1 Diabetes (T1D). Throughout my practicum period, I will collaborate with my preceptor to develop and implement a QI project focused on improving 1D and pediatric patient management within primary care settings.
The identified problem of interest is Juvenile Diabetes also known as Type 1 Diabetes (T1D). T1D, unlike type 2 diabetes, is an auto-immune-mediated chronic condition linked to the destruction of insulin-producing B-cells in the pancreas (Eizirik et al., 2020). T1D is an issue of concern due to the growing prevalence of the condition, with a 3-4% rate reported in the last few years (Norris et al., 2020). The loss of function of the B-cells in the pancreas causes the body to lose its ability to secrete insulin. This loss creates a dependency on life-long insulin replacement therapy. It is a notable problem in pediatric care and an issue of interest as it is a chronic condition that requires long-term individualized management (Speight & Pouwer, 2023). Its prevalence has also grown over the years and is a major risk factor for other chronic conditions, including cardiovascular conditions and type 2 diabetes. It causes a strain on family dynamics and finances and a lower quality of life for the child.
The proposed QI project will include the implementation of the T1D Exchange Quality Improvement (T1DX-QI) Collaborative program in the diabetes care clinic. The T1DX-QI is a collaborative, data-driven, continuous quality improvement program that currently involves the efforts of 50+ collaborating clinics (Ginnard et al., 2021). The aim of the T1DX-QI collaborative program is to improve the outcomes of T1D care through a multidisciplinary collaborative approach. Such outcomes include better T1D-related outcomes, better quality of care, and equitable access to care.
The preceptor has been a great guide throughout the practicum hours, including guiding on the process of search and review of existing literature to develop evidence to guide decisions and actions in practice, including developing a PICO(T) question and a search strategy. The developed PICO(T) question is “In children with type 1 diabetes (P), does the T1D Exchange Quality Improvement Collaborative program (I), compared to standard diabetes care (C), significantly improve glycemic control, adherence to medication, and quality of life (O) in 12 months (T)?” The selected databases that will be used for the literature search as guided by the PICOT question are PubMed and Cochrane Library. The keywords and keyword synonyms to be used for research will include juvenile diabetes and Type 1 diabetes, children and adolescents, T1D Exchange Quality Improvement Collaborative program, standard care and routine treatment, glycemic control and blood sugar control, medication adherence, and quality of life.
Current research supports the implementation of the T1DX-QI collaborative to address and improve T1D outcomes. A study by Akil et al. (2021) explores the current evidence on personalized medicine in relation to T1D care. The authors argue that there is a need for personalized T1D diagnosis and treatment in order to achieve personalized risk stratification, pre-clinical detection, and individualized care focused on preventing pancreatic destruction. Alonso et al. (2020) provide guidance on the establishment of T1DX-QI while DeSalvo et al. (2023) provide evidence on disparities in access to T1D care with a focus on demographics access and use of continuous glucose monitors (CGM). Notably, individuals from low SES have limited access to CGM and experience poor outcomes. DeSalvo et al. (2023) note that the T1DX-QI has proved to have the potential to improve equity in access and use of CGM, hence reducing disparities in T1D care outcomes. Additionally, Ginnard et al. (2021) present the T1DX-QI as a collaborative framework that significantly improves care delivery and health outcomes in T1D patients.
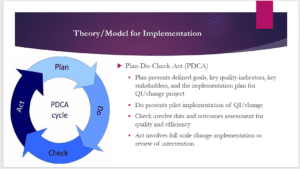
The selected model to guide the implementation of the QI project (T1DX-QI) is the Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA). The PDCA cycle has four stages. Stage one involves planning for the implementation of the project, including the definition of goals, identification of key quality indicators and key stakeholders, and development of the implementation plan for the QI/change project. Stage 2 involves the doing stage, in which the project is implemented on a pilot basis and data is collected. Stage 3 involves the check step, which is the analysis of data and assessment of outcomes for improvement of quality and efficiency after implementing the project. The final stage is the act stage, in which the project is implemented at a full scale or reviewed for further modifications based on the analyzed data and outcomes.
The implementation of the T1DX-QI will be based on the PDCA model. The first stage of implementing the collaborative program will involve assessing the available resources within the clinic, setting and defining the project’s goals, and identifying the key measures and stakeholders for the project. The second stage is the will involve the actual implementation of the TIDX-QI collaborative within the clinic. The program will be implemented on a pilot basis, and data on outcomes will be collected. The third stage of the implementation will include continuous review and assessment of the collected data as well as the progress of the program. Finally, after the data has been analyzed and reviewed, a full-scale integration of the best practices identified based on the implementation of the T1DX-QI Collaborative will be established within the daily T1D care in the clinic.
Measures for the project will include changes in HbA1c levels with the program, effectiveness of glycemic control and adherence to T1D management protocols, as well as patient-reported levels of satisfaction and patient and provider experiences with the T1DX-QI Collaborative Program. Focus will also be paid to perceived improvements in quality of care, the reduction of disparities in the access to T1D care, and the reduction in the costs of delivering and accessing T1D care.
In summary, T1D will be the health problem of interest and focus during the practicum. This is because its prevalence is growing, and it is also a risk factor for major chronic conditions, including an increased risk for T2D and associated complications. It also increases the costs of care and leads to a reduced quality of life. The proposed QI focuses on implementing the T1DX-QI collaborative program on a pilot basis based on the PDCA model. The proposed measures for the QI project include process, care, patient, and resource measures.
ORDER A PLAGIARISM-FREE PAPER HERE
We’ll write everything from scratch
Question
This week, you will finalize your PowerPoint summarizing your entire QI project.
Additional details for each project can be viewed in the Course Projects Module
This week, you will finalize your PowerPoint summarizing your entire QI project.
Additional details for each project can be viewed in the Course Projects Module
Rubric
PowerPoint Presentation Rubric
PowerPoint Presentation Rubric
Criteria Rating Pts
This criterion is linked to a Learning Outcome Finalized PowerPoint or poster presentation of the proposals including the title and author, background, research question, literature review, change theory, and stages of implementation based on the selected change theory.(9 slides)

Comprehensive Summary of a Quality Improvement Project- From Practicum to Implementation
80 to >70.0 pts
Excellent
Power points/or poster presentations include all components listed.
70 to >40.0 pts
Needs Some Improvement
The finalized PowerPoint/poster presentation is missing one component listed.
40 to >10.0 pts
Needs Significant Improvement
Finalized power points or poster presentations are missing more than one component listed.
10 to >0 pts
Poor
Finalized PowerPoint/or poster presentation, is missing one or more components listed.
80 pts
This criterion is linked to a Learning Outcome Elements of the Power Points or Poster presentation Format
20 to >16.0 pts
Excellent
The prescribed number of slides in presentation: Includes a title side, summary slide, and reference slide in APA. Each slide has the appropriate amount of text following 7 lines,7 words per line. Background does not detract from text or other graphics. Choices of font enhances readability. Uses professional graphics to add value to the presentation.
16 to >12.0 pts
Needs Some Improvement
A number of slides in the presentation is less than prescribed, by 1-2 slides One of the following may be missing: title slide, summary slide, or reference slide. Most slides have the appropriate amount of text (Follow the 7×7 rules) Background may detract from text or other graphics. Some font formats may detract from readability. The graphics overall look professional.
12 to >4.0 pts
Needs Significant Improvement
A number of slides is significantly less than prescribed by greater than or equal to 3 slides. More than one of the following is missing: title slide, summary slide, reference slide. Many slides have too little or too much text. Background detracts from text and/or graphics. Font format varies from slide. The graphics look less than professional.