Cloud Computing Fundamentals and Key Security Considerations for a Successful Migration
Hello. Welcome to this presentation on cloud computing.
Cloud computing is a transformative technology that has reshaped how organizations manage their digital infrastructure. Cloud computing is the delivery of various computing services and resources over the Internet. These services encompass servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, and intelligence. The evolution of cloud technology since its inception in the late 1990s has been profound. It has become a cornerstone of modern business operations, offering scalability, flexibility, and economies of scale. The significance of cloud computing in today’s digital landscape cannot be overstated, as it allows organizations to innovate faster, efficiently allocate resources, and achieve cost savings. Accordingly, this presentation highlights the key cloud service models: Software as a Service (SaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), and Data as a Service (DaaS). Understanding these models is pivotal for organizations considering cloud adoption as they cater to distinct needs and use cases. The connection between cloud computing and cybersecurity is emphasized. As organizations increasingly migrate to the cloud, cybersecurity professionals need to grasp the implications and security measures associated with cloud technology.
Cloud computing models define how cloud services are structured and delivered, catering to various organizational needs. SaaS is exemplified by web-based software applications accessed over the Internet. Prominent examples include Microsoft Office 365 and Salesforce. Users can access these applications without installation, making them highly convenient. Next, PaaS provides a platform for developers to build, deploy, and manage applications (Bokhari et al., 2016). Platforms like Google App Engine and Heroku offer a framework that simplifies development, allowing developers to focus on coding rather than infrastructure management. Third, IaaS offers fundamental computing resources such as virtual machines, storage, and networking. Leading IaaS providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Microsoft Azure enable users to provision resources on-demand, offering flexibility and scalability. Lastly, DaaS grants users access to data from anywhere via the Internet. For instance, Bloomberg Professional Services provides financial data on demand. DaaS is valuable for organizations requiring real-time access to data without managing complex databases. Notably, understanding these service models is critical for organizations planning to migrate to the cloud, as each model serves distinct purposes. It allows them to decide which model best aligns with their requirements and objectives.
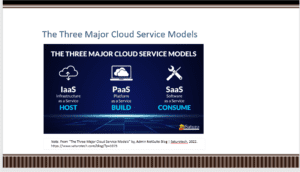
The three major cloud service models: Iaas, Paas, and SaaS.
Regarding resource requirements, local resources typically demand substantial upfront investments in hardware, software, and maintenance. This can pose a financial burden for organizations, especially startups. In contrast, cloud resources follow a pay-as-you-go model, reducing initial capital expenditure. Next, local setups offer direct control over infrastructure and data, allowing organizations to customize and fine-tune resources. On the other hand, cloud resources rely on service providers, relinquishing some control but providing convenience. Regarding network requirements, cloud solutions necessitate stable internet connectivity. A disruption in the internet connection can hinder access to cloud resources. Local setups, while not dependent on internet connectivity, require efficient local network infrastructure. Further, cloud services often offer robust security measures, with providers investing heavily in cybersecurity. However, the reliance on third-party providers can introduce concerns about data privacy and security breaches. Local systems, while less exposed to internet-based attacks, face their own security risks, such as physical breaches and outdated security measures. Concerning attack mitigation, cloud providers typically implement advanced security measures to mitigate a wide range of attacks. They continuously update and patch their systems to protect against emerging threats. Local systems require proactive security management to address vulnerabilities. Moreover, the overall vulnerability of cloud environments differs from local setups. Cloud environments can be more vulnerable to internet-based attacks, while local systems face risks from physical threats and outdated security measures. Understanding these comparisons is essential for organizations to make informed decisions about resource allocation and security measures, considering factors like cost, control, and vulnerability.
Virtualization involves the creation of virtual instances of servers, storage, and networking components. It allows for the efficient utilization of physical resources and enables flexibility in resource allocation. Virtualization is the underlying technology that enables cloud computing to function efficiently. It abstracts physical hardware, allowing multiple virtual instances to run on a single physical server. This enhances resource management, scalability, and cost-efficiency. Leading virtualization platforms include VMware, Microsoft Hyper-V, and Oracle VM (Odun-Ayo et al., 2017). These platforms provide the necessary tools and infrastructure for creating, managing, and maintaining virtual environments. Virtualization offers numerous advantages, including cost savings, improved disaster recovery, faster server provisioning, and reduced hardware needs. It allows organizations to optimize resource utilization and streamline IT operations. While virtualization enhances resource management, it introduces security considerations. The hypervisor, a key component of virtualization, must be secured to prevent unauthorized access and breaches. Isolation between virtual instances is crucial to prevent data leaks. Organizations should prioritize regular updates, secure configurations, and continuous monitoring to maintain security in virtualized environments. These practices ensure that vulnerabilities are addressed promptly. Understanding virtualization platforms is essential for organizations migrating to the cloud, as it forms the foundation of cloud infrastructure. It enables efficient resource allocation and management while requiring a focused approach to security.
Let’s now explore the various deployment models in cloud computing, elucidating their characteristics and highlighting the factors that influence the choice of deployment model. To begin, a private cloud is exclusively used by a single organization. It offers maximum control over resources and security. Private clouds are ideal for organizations with stringent data security and compliance requirements. However, they may entail higher costs due to dedicated infrastructure. Next, public clouds provide services over the public Internet and are available to anyone. Providers like Microsoft Azure and AWS offer a wide range of services. Public clouds are cost-effective and scalable, making them suitable for startups and businesses with variable resource demands (Patel & Kansara, 2021). However, they may raise concerns about data security and compliance. Third, community clouds are shared infrastructures catering to specific community groups. These groups share common concerns and compliance requirements. They allow for resource sharing among organizations with similar needs, reducing costs while maintaining security and compliance. Fourth, hybrid clouds combine elements of both private and public clouds. They offer flexibility by allowing data and applications to move between private and public environments. This model suits organizations with varying resource demands, enabling them to balance control and scalability. Notably, the choice of deployment model depends on several factors, including security requirements, cost considerations, control over resources, compliance obligations, and scalability needs. Organizations must weigh these factors to determine the most suitable model. Also, each deployment model has its unique security challenges. Private clouds offer more control but require robust in-house security measures. Public clouds benefit from provider security but expose data to the Internet. Hybrid clouds demand the integration of security measures across both environments. Understanding the deployment models is crucial for organizations when making informed decisions about their cloud strategy. Each model has advantages and trade-offs, making it essential to align the choice with organizational objectives and needs.
Service-oriented architecture (SOA) is a framework that facilitates the creation of business applications by enabling the interaction of services over a network. It is based on the concept of breaking down applications into smaller, modular services that can be accessed and reused (Bahrami & Singhal, 2015). SOA is crucial in achieving interoperability between disparate systems. By encapsulating functionality into services with well-defined interfaces, different systems can communicate seamlessly, regardless of their underlying technologies. Also, SOA is instrumental in building complex business applications that rely on integrating various services. It allows organizations to create applications that are agile, scalable, and adaptable to changing business needs. Additionally, SOA enhances scalability by enabling the addition or removal of services as needed. This flexibility is vital in cloud computing, where resource demands can fluctuate rapidly. SOA also acts as a bridge between legacy systems and modern cloud services. It enables organizations to leverage their existing investments in technology while incorporating new cloud-based services. Noteworthy, security is a critical consideration in SOA. It involves securing each service and ensuring data confidentiality, integrity, and availability during service interactions. Understanding SOA is essential for organizations planning to adopt cloud computing, as it provides the framework for building scalable and interoperable applications. SOA promotes agility and flexibility, aligning well with the dynamic nature of cloud services.
Security is a top priority in cloud computing due to the potential exposure of sensitive data and resources. Organizations must mitigate risks to protect their assets. Cloud security challenges include data breaches, insufficient identity and access management (IAM), insecure interfaces and APIs, system vulnerabilities, advanced persistent threats (APTs), and legal and regulatory compliance. To address these challenges, organizations employ a range of security measures. Encryption is used to protect data at rest and in transit. IAM solutions are implemented to control user access and privileges. Regular security audits and compliance checks ensure that security measures remain effective. Employee training is essential to educate staff on security best practices. This includes recognizing and responding to potential threats and adhering to security policies. Also, having a well-defined incident response plan is critical for dealing with security breaches. It outlines the steps to take in the event of a security incident, ensuring a prompt and organized response. In addition, organizations should allocate resources to support security efforts. This includes investing in security tools, personnel, and ongoing training to stay updated with evolving threats. Security is an ongoing process in cloud computing, and organizations must remain vigilant and proactive in protecting data and resources. Implementing robust security measures and fostering a security-conscious culture are essential for secure cloud adoption.
Cloud storage offers scalable, flexible, and cost-effective solutions for organizations to store their data. It includes services such as backup, archiving, and disaster recovery. Effective data governance is crucial in cloud computing. It involves defining data ownership, access control, and data lifecycle management. Organizations must establish clear policies for data usage, retention, and disposal. Also, ensuring data integrity is paramount in cloud storage. Data integrity measures validate the accuracy and consistency of data stored in the cloud, preventing data corruption and unauthorized alterations. Similarly, robust security measures are essential to protect sensitive data stored in the cloud. This includes implementing encryption to safeguard data both at rest and in transit. Access controls and authentication mechanisms ensure that only authorized users can access data. Regular security assessments and audits help identify vulnerabilities and ensure compliance with security standards. Moreover, cloud storage solutions often include data backup and disaster recovery services. These services enable organizations to create copies of critical data and applications, ensuring business continuity in case of data loss or system failures.
Additionally, organizations must adhere to data protection regulations and standards specific to their industry. For example, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) imposes strict requirements on the handling of personal data. Compliance with these regulations is essential to avoid legal and financial repercussions. Besides, protecting user privacy is a fundamental consideration in cloud data management. Organizations must have mechanisms to manage user consent, data access, and data rights. Transparency in data handling practices builds trust with users. Beyond compliance, organizations should also be aware of data sovereignty and jurisdiction issues. Data stored in the cloud may be subject to the laws and regulations of the country where the data is located. Understanding these legal aspects is crucial for risk mitigation. In sum, effective storage and data management are foundational to successful cloud adoption. Organizations should establish comprehensive data governance policies, implement robust security measures, and ensure compliance with relevant regulations to safeguard their data in the cloud.
Data privacy is a paramount concern in cloud computing. Organizations must adhere to data protection regulations and standards, such as GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA, depending on their geographic location and the nature of the data they handle. Organizations must be aware of data sovereignty issues when choosing cloud providers and data center locations. Data sovereignty refers to the legal concept that data is subject to the laws and regulations of the country where it is located. Also, managing intellectual property rights is crucial when storing data in the cloud. Organizations should clearly define ownership of data and intellectual property rights in contracts with cloud service providers. In addition, many jurisdictions require organizations to promptly notify authorities and affected individuals in the event of a data breach. As such, establishing incident response plans and breach notification procedures is essential to compliance. Further, organizations should conduct regular legal audits to ensure ongoing compliance. These audits assess adherence to data protection laws, contract terms, and the organization’s own policies. Another crucial consideration lies in user consent and data rights. Managing user consent and data rights is essential. Organizations should provide transparency about data usage, allow users to control their data, and honor requests for data access and deletion (Kerr & Teng, 2018). Navigating the legal and privacy landscape in cloud computing requires a deep understanding of regional and industry-specific regulations. Failure to address these considerations can result in legal liabilities, reputational damage, and financial penalties.
ORDER A PLAGIARISM-FREE PAPER HERE
We’ll write everything from scratch
Question
As organizations increasingly move toward cloud technology, a cybersecurity professional should be familiar with the effect(s) it has on security.
You have been asked by your company to explain the fundamentals of cloud computing and related security issues because your company is migrating to the cloud.
Cloud Computing Fundamentals and Key Security Considerations for a Successful Migration
Create a presentation of 9 slides that explain cloud services.
Address the following:
- Describe each type of service/model of cloud computing.
- Compare and contrast: local resource requirements, local control, network requirements, and security (attacks, mitigations, overall vulnerability).
Additionally, ensure you cover the following topics in your presentation:
- Virtualization platforms
- Cloud services (SaaS, PaaS, DaaS, IaaS)
- Service-oriented architectures
- Deployment models (private, public, community, hybrid)
- Security, storage, legal/privacy issues
Support your presentation with a minimum of Five scholarly resources.
Include a title page, presenter’s notes, and reference page.
The digital presentation should include graphics that are relevant to the content, visually appealing, and use space appropriately.