Data Analysis and Quality Improvement Initiative Proposal
Hello and welcome to today’s presentation. It is my pleasure to welcome you to this session. The current session is dedicated to the pivotal role of data analytics in quality improvement campaigns. Notably, healthcare professionals are always looking for improvements in patient outcomes and provide the best service possible. Data-driven decision-making is the key that enables us to identify problematic areas, evaluate progress and, lastly, replace it with positive change. The analysis of the dashboard data in this presentation will allow us to diagnose healthcare problems, develop better care quality improvement initiatives, and, eventually, improve care quality and patient outcomes. Thus, we will delve into “evidence-based quality improvement” and discuss how we can apply it to create substantial changes in healthcare delivery.
Here is an outline of the presentation. We will begin by understanding data analysis. We will then look at the identified healthcare issue. Next, we will discuss the quality improvement initiative proposal, along with interprofessional perspectives. We will then look at the collaboration strategies. Finally, we will look into assumptions and knowledge gaps.
Organized Data Examination: The systematic arrangement of data helps in having a holistic look at the types of medication errors, their frequencies, and the factors that led to them (Mutair et al., 2021). Visual aids, including charts and graphs, that enhance understanding and give the ability to share the key findings of medication safety to stakeholders help develop a common understanding of both the medication safety challenges and the available avenues for improvement between multi-professional teams.
Quality Improvement Metrics: A major performance marker is the error rate, safety protocol, and medication reconciliation accuracy, which are key indicators when it comes to medication safety standards (Singh et al., 2023). These continuous measuring processes help healthcare organizations to timely identify and prioritize critical areas and drive steps for improvements to have optimal patients’ care.
Trend Analysis: Trend analysis provides an overall picture of whether error rates have decreased over time. This allows one to evaluate if the applied remedies were efficient and if there remain any latent issues (Singh et al., 2023). Future-oriented approach gives health teams an opportunity to introduce specific measures to lessen hazards and enhance the degree of safety for patients. As a result, a culture of learning and continuous improvement is developed.
Outcome Measures: Comprehensive outcome measures envisage adverse events, patient harm, and satisfaction, thereby allowing an overall evaluation of medication safety outcomes. The precise measurement of rates demands careful data collection and analysis, which in turn enables healthcare institutions to assess the effectiveness of the interventions they introduce and prioritize programs for patient safety and enhancing quality of care.
Process Stability Assessment: Stability assessment evaluates the stability and dependability of medication management processes, pinpointing variations or failures that might endanger patient safety (Singh et al., 2023). Through timely identification and mitigation of deviations from evidence-based processes and the implementation of interventions that improve reliability, health organizations ensure the safety of medications throughout the care cycle.
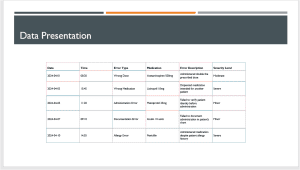
The table above shows a selected data set analyzed in this proposal.
Based on the data analysis, the major healthcare problem is the occurrence of medication errors within the healthcare facility. Medication errors occur throughout the medication process, which includes prescribing, dispensing, giving, and monitoring medications (Tariq & Scherbak, 2023). The causes of these mistakes may include miscommunication, poor staff training, complicated drug regimens, and system failures. The analysis of the data from dashboards exhibits a concerning rate of medication mistakes, which can be fatal to patient safety and treatment quality.
To prevent medication errors is of paramount importance because of their wide-ranging consequences on patient outcomes, safety, and the healthcare system as a whole. Errors in medication causing adverse drug reactions, treatment complications, extended hospital stays, as well as patient harm or death are all among the consequences (Tsegaye et al., 2020). In addition, medication errors add up to the higher costs of healthcare because they mostly require other medical procedures, re-admissions to the hospital, and legal expenses. Overlooking the problem undermines patient trust, spoils the reputation of the healthcare facility, and might lead to sanctions and fines
The proposed quality improvement project strictly aligns with a variety of benchmarks established by federal healthcare policies such as the Affordable Care Act and CMS and Joint Commission regulations. These benchmarks should cut across a wide range of spheres relating to medication safety and patient care that include elimination of medication errors, application of evidence-based practices, and compliance with regulatory requirements for medication management. Through the use of the mentioned guidelines, the medication safety initiative guarantees regulatory compliance and the development of a culture of unending improvement in medication safety within the healthcare setting. Additionally, it emphasizes patient safety by improving overall medication management processes and aligning with initiatives conducted by the National Quality Forum (NQF) and the Institute for Healthcare Improvement (IHI).
The introduction of strategic process adaptations forms a fundamental part of the proposed measures, including activities such as developing standardized medication reconciliation protocols, integration of barcode scanning techniques for medication administration, and establishment of effective mechanisms for reporting and handling medication errors promptly. These alterations aim at standardizing procedures for medication management, facilitating workflow efficiency, and reducing error rates, thus creating a patient environment that is amenable to success.
Leveraging evidence-based practices, the program will include interventions such as deploying clinical decision support systems, conducting routine medication safety audits as well as delivering ongoing staff education on new practices in medication management (Shahmoradi et al., 2021). This evidence-based approach is based on established professional guidelines and valid research findings, which provide the healthcare organization with a well-structured plan for driving sustained improvement in medication safety outcomes and creating a culture of permanent learning and adjusting.
Evaluating the effectiveness of the current quality improvement programs against the benchmarks and quality indicators is necessary to gauge how they are handling medication errors and improving patient safety, among others. The initiative aims to use the already established metrics and benchmark models from authoritative sources such as the National Quality Forum to objectively review the existing initiatives, find change areas, and make sure the plans are coordinated with the best practices and the existing industry standards accordingly.
A thorough examination of issues highlights both the systemic (resistance of staff to change, limited resources, and logistical challenges of coordinating interprofessional activities) and many barriers to quality improvement. Zajac et al. (2021) indicate that overcoming hurdles like these requires a different type of leadership, better communication strategies, and collaborative problem-solving methods so that the organization may build a culture of innovation, resilience, and adaptiveness. Tackling these problems directly is the initiative’s objective, which is to enable sustainable change and consequently achieve noteworthy effects in medication safety indicators, with the primary target of upgrading the quality of care rendered to patients.
Integration of healthcare practitioner viewpoints and contributions from the professionals involved in the quality improvement project that focuses on eliminating medication errors is inevitable. Every member of the team has a unique skill set and perspective, which is a true blessing when it comes to addressing a complex healthcare problem (Kozlowski & Ilgen, 2019). Case in point, pharmacists have a crucial role in ensuring the accuracy and safety of medication orders. On the other hand, nurses are on the frontline of medication administration and have valuable input on workflow processes and patient interactions. The doctors, in turn, provide their clinical skills in choosing medications and monitoring response to treatment, while quality improvement specialists facilitate the implementation of evidence-based practices and monitor progress.
A collaborative attitude is important in order to define actions and responsibilities for each team member. Pharmacists may take the role of leading the processes that standardize medication administration protocols so that orders are properly transcribed and dispensed. Nurses can be entrusted with roles such as medication reconciliation, identification of patients and their medication orders, and patient education on medication schedules and side effects, along with other related areas. Physicians might be asked to review and approve medication orders, talk to other healthcare professionals on complex cases, and evaluate the response of patients to medications (Zajac et al., 2021). Medication error improvement specialists coordinate interprofessional dialogue, collect and analyze data on medication errors, identify areas for improvement, and implement evidence-based interventions. By clarifying the specific roles and duties of each team member, the initiative would enable an interprofessional team that draws upon its collective competencies and assets to achieve significant improvements in medication safety.
The first approach is to create communication channels among healthcare professionals and make them available for the sharing of ideas, lessons, and tips regarding medication safety in the organization. By using team huddles or regular meetings, one can create synergy, permitting team members to discuss patient history in more detail, review medication orders, and take advantage of their collective wisdom. Moreover, utilizing these communication tools, namely, electronic health records (EHRs) and secure messaging platforms, can empower the convenient flow of information and timely updates on pro-inflammatory drug matters (Aguirre et al., 2019). Through collaboration and the use of communication tools and strategies, health organizations will create teams of people who are curious and creative, which, consequently, increases medication safety and better health outcomes.
First, organizing regular interdisciplinary meetings is crucial for discussing progress, sharing insights, and mutually handling challenges. These meetings contribute to the common ground and, therefore, clear goals and objectives, as well as a collaborative spirit.
ORDER A PLAGIARISM-FREE PAPER HERE
We’ll write everything from scratch
Question
Assessment 3
Data Analysis and Quality Improvement Initiative Proposal
Instructions
Resources
Activity
Attempt 1
available
Attempt 2
Attempt 3
Make a quality initiative proposal (7-10 PowerPoint slides) through a presentation, interpreting and communicating dashboard data to support the proposal.
Collapse All
Introduction
Healthcare providers are perpetually striving to improve care quality and patient safety. To accomplish enhanced care, outcomes need to be measured. Next, data measures must be validated. Measurement and validation of information support performance improvement. Healthcare providers must focus attention on evidence-based best practices to improve patient outcomes.

Data Analysis and Quality Improvement Initiative Proposal
Health informatics, along with new and improved technologies and procedures, are at the core of all quality improvement initiatives. Data analysis begins with provider documentation, researched process improvement models, and recognized quality benchmarks. All of these items work together to improve patient outcomes. Professional nurses must be able to interpret and communicate dashboard information that displays critical care metrics and outcomes along with data collected from the care delivery process.