Dynamic Complexity in the Workplace Environment
Senge (2006) avers that dynamic complexity produces a negative effect in terms of time elongation, shortage, and loss. Observing dynamic complexity is impossible since only the outcomes from the situation are measurable. Besides, historical data cannot predict the impact of dynamic complexity. Treating dynamic complexity before it negatively impacts operations requires diagnostics to reveal its causes and potential effects on a system.
Personal Experience
Workplace distractions due to movements and conversations are synonymous with many offices. Lately, I have experienced this dynamic complexity in my workplace. As a result, we have to wear noise-cancelling headphones to curb the disruption. Although this appears like a solution from the outset, it does not help much since having headphones on while working reduces focus and hampers productivity.
Senge’s Criteria for Dynamic Complexity
According to Yasarcan (2023), one of the criteria for determining dynamic complexity is if an action has a different set of impacts in the short run and in the long run. Putting on headphones to curb distractions at the office sounds like an effective solution in the short run. However, in the long run, the action hampers teamwork and collaboration as team members do not communicate effectively with one another.
Inter-Relationships between Major Elements in the System
There are no linear-causal chains in systems thinking. Instead, the outcomes of a dynamic complexity are caused by subtle interrelationships between elements in the system (Jagustović et al., 2019). The dynamic complexity case explained above shows that different elements contribute to office distraction. First, improper office organization forces office users to move from one point to another, causing disruptions. Also, external factors from the surrounding environment may cause disruptions.
How the Structure of a System Impacts Its Behavior
One of the main highlights of systems theory is that structures influence behavior. An excellent example of how systems may influence behavior in an organizational setting is when opinions are limited in a hierarchical organization (Tran & Tian, 2013). For the dynamic complexity mentioned above, different factors, infrastructure, logistics, and workspace influence behavior. The open-office system encourages disruptions at the office.
Altering a Structure to Improve its Performance
Organizations should continually learn new ways to eliminate weaknesses in their operational systems. For office disruption cases, the organization may improve operations by offering each team its equipment to reduce movement around the office. Also, acquiring new space to prevent team members from working from the same room will help curb disruptions.
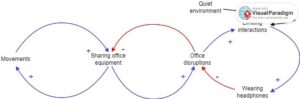
Causal Loop Diagram
The causal loop diagram shows how hard it is to solve a dynamic complexity. The diagram has balancing loops that limit movement in a given direction. For instance, the diagram indicates that reducing office interaction helps in reducing disruptions.
Conclusion
Treating dynamic complexity requires a diagnosis that extends beyond the obvious. As shown by the office distraction example, more underlying elements contribute to the noise. As a result, wearing noise-canceling is an obvious solution that may not bring the intended results. However, with proper diagnostics, the distraction may be solved through proper office space management and ensuring each team works from its separate space.
References
Jagustović, R., Zougmoré, R. B., Kessler, A., Ritsema, C. J., Keesstra, S., & Reynolds, M. (2019). Contribution of systems thinking and complex adaptive system attributes to sustainable food production: Example from a climate-smart village. Agricultural Systems, 171, 65–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agsy.2018.12.008
Senge, P. M. (2006). The fifth discipline: The art and practice of the learning organization. Doubleday.
Tran, Q., & Tian, Y. (2013). Organizational structure: Influencing factors and impact on a firm. American Journal of Industrial and Business Management, 03(02), 229–236. https://doi.org/10.4236/ajibm.2013.32028
Yasarcan, H. (2023). The four main elements of dynamic complexity. System Dynamics Review, 39(2), 171–179. https://doi.org/10.1002/sdr.1731
ORDER A PLAGIARISM-FREE PAPER HERE
We’ll write everything from scratch
Question

Dynamic Complexity in the Workplace Environment
Overview:
System dynamics are when structure determines behavior, and there are time delays and absences of feedback/balancing loops. For this assignment, you will discuss a situation where there is dynamic complexity, as well as complete a causal diagram of the situation.
Instructions:
- Please cover the following topics in your paper:
- Discuss an example of dynamic complexity that you have experienced at work. Be specific
- Describe which of Senge’s criteria this event meets to be considered “dynamic ”
- Discuss the interrelationships. Address how each major element of the system impacts the other elements and the performance of the system
- Explain how the structure of the system impacts its behavior
- Describe how you would alter the current structure to improve system performance.
- Draw a causal loop diagram of this situation. Include balancing and/or feedback loops. Make sure you discuss the role balancing loops play in your narrative