Macroeconomics Simulation
For the benefit of the incoming administration, I submit this report to document, analyze, and interpret the macroeconomic policy decisions I made as the chief economic policy advisor of Econland. This document aims to further our national prosperity by deepening our understanding of the relationship between macroeconomic policies and their consequences for our citizens. The report includes a thorough accounting of the major fiscal and monetary policy decisions made over each of the seven years of my term, as well as an explanation of the underlying rationales for those decisions and the resulting impacts of those policies.
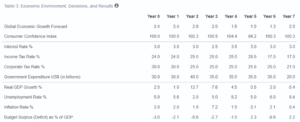
The table above summarizes the macroeconomic climate of Econland over my term. I worked with a volatile scenario where Econland residents chose to hold more foreign assets relative to partner countries. The overall state of the economy was good, save for some periods where a bit of recession was experienced. The economy had improved significantly by the end of the seven years. As a result, I was given a staggering rating of 70%, implying that my role as an economic policy advisor was approved.
There was a severe recession during the administration’s third year, as the country registered a negative GDP growth of -7.6%. I advised the government to employ expansionary fiscal policy to restore the economy. One of the fiscal expansionary strategies I urged the government to use was to lower taxes. Reducing taxes enhances aggregate demand, which then fuels economic growth.
Specifically, the government offered tax stimulus rebates. Consequently, people were required to pay less for products and services. As a result, they had more disposable income, which they used to buy more products and services. That also means companies receive more revenue, hire more people and reduce unemployment (Hemming, Kell & Mahfouz, 2002). As the demand for labour rose, the competition in the labour market among employers also increased. Although the unemployment rates remained high after the third year, the real benefits were a salary rise and improved employee conditions to reduce the attrition rate.
Another strategy employed to deal with recessions was increased government spending. As the government built more highways and other infrastructure, the level of employment went up. The net effect of both expansionary fiscal policies was increased aggregate GDP.
Interest Rates
Interest rates were lowered from 3% to 2.5% during the third year. Lowering interest rates makes borrowing money cheaper (Hemming, Kell & Mahfouz, 2002). Individual investors and companies could borrow more and invest as the interest rate dropped. Besides, a low-interest rate discouraged economic players from saving. Instead, the money was used for investing or buying goods and services. The result was a vibrant economy and increased aggregate GDP.
References
Hemming, R., Kell, M., & Mahfouz, S. (2002). The effectiveness of fiscal policy in stimulating economic activity: A literature review. Available at SSRN 880868.
Mankiw, N. G. (2021). Principles of economics (9th ed.). Cengage Learning.
ORDER A PLAGIARISM-FREE PAPER HERE
We’ll write everything from scratch
Question
The Simulation Checkpoint Assignment in this course directly supports your success on the course project. You will play the simulation game, create the image file of your simulation report, and discuss learned concepts and experiences in your submission.

Macroeconomics Simulation
Prompt
For this assignment, you will play the first run of the Macroeconomics Simulation: Econland from Harvard Business Review, in which you will act as policy adviser for the fictional country of Econland. Select the “Base Case” scenario for this practice run. You may play the simulation as many times as you like. This will directly support your success in your course project, which is due in Module Eight.
In your submission, remember to include the image of your simulation report. For help, see How to Submit an Image File of Your Report. Then, reflect on the decisions you made in the simulation and address the following government intervention options in your submission:
- Macroeconomic Indicators: During the simulation, you made decisions concerning government spending. Discuss the impact of your choices on key macroeconomic indicators such as real GDP growth and unemployment. Refer to the graphs “Real GDP Growth” and “Unemployment Rate” from your simulation results to illustrate the impact.
- Interest Rates: Describe how your changes in interest rates impacted inflation and other key macroeconomic indicators used in the simulation. Refer to the “Inflation Rate” graph from your simulation results.