Oligopolies
Hello Class,
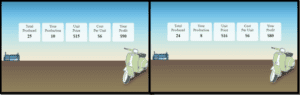
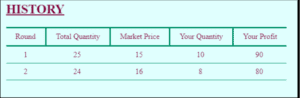
Playing the simulation game has aided me in understanding the competition in the game and how the economic model works. Using the simulation, I learned that the season’s incentive equals the scooter’s number. Furthermore, the profits show the distinction between the market price of the season and my cost per unit made.
Features of an Oligopolistic Market
The oligopolistic market has fewer but vital features in the market. Firstly, it is an industry dictated by a few numbers companies, and only a few sellers dominate most of the sales in the industry. Secondly, an oligopolistic market has more significant barriers to entry. To enter the market, one needs high start-up capital to run and grow (Mankiw, 2021). Furthermore, one needs more advantages than competitors to lure more customers into their market. One of the most vital features of an oligopolistic market is its interdependence. Interdependence means that when one business is impacted by the different changes experienced in the market, other companies are also affected. Regarding oligopolistic needs, firms usually maintain a constant price to avoid losing benefits that may present themselves.
Are you interested in an unpublished edition of the assignment ? Get in touch with us. Our team of experts is ready to help.
Price Setting
For oligopolies to set their prices, the owner has to choose from two choices: the effect of the cost of the output impact. The price effect increases production by raising the total amount of products sold, leading to lower product prices and profits. The output impact is the price rising above the marginal cost. If a product is sold at the exact rate, the gain will increase (Mankiw, 2021). When the output impact exceeds the effect of the price, the firm owner expands the production, and when the price effect prevails over the output impact, the owner refrains from increasing the production.
Differentiating A Firm in An Oligopolistic Market and Monopolistic Competitive Market
Different features differentiate a firm in an oligopolistic market from a monopolistic market. First, oligopolies have fewer firms, including more significant barriers that stop other firms from entering the market. On the other hand, monopolistic competition has several firms that supply the same products and allow free exit and entry into the market (Mankiw, 2021). Examples of oligopolies include cell phone barriers, Sprint, and T-Mobile. The mentioned companies significantly impact the industry in that they work together to gain as a whole, making the prices go higher. Examples of monopolistic competition include hotels, bars, and restaurants. All the above companies have a lot of competitors, but each offers different types of food and atmospheres for the customers to experience.
Reference
Mankiw, N. G. (2021). Principles of microeconomics (9 edition). Cengage.
ORDER A PLAGIARISM-FREE PAPER HERE
We’ll write everything from scratch
Question
An oligopoly is a market structure in which only a few sellers produce similar or identical products. Oligopolies are price-setters and can collude to behave like a monopolist.

Oligopolies
First, play the simulation game Cournot in the MindTap environment. In this discussion, you will share your experiences playing that game. Your work in this discussion will directly support your success on the course project.
In your initial post, include the image of your simulation report in your response. See the How to Submit a Simulation Report Image PDF document for more information. Then, address the following questions:
- What are the main features of an oligopolistic market?
- How do oligopolies set their prices?
- Explain how you can distinguish a firm in an oligopolistic market from a monopolistic competitive market. Provide examples to illustrate.
In your responses, comment on at least two posts from your peers by providing examples from the news of oligopolistic markets. Compare and contrast with examples of monopolistic competitive markets.