Tracking System Solution For Swift Service Company
1. Project Outline
1.1 Company Overview
Swift Services is a diversified freight company established in mid-1987 by Nerv Thomas (Swift Services, n.d.). Currently, the company is led by Thomas and Melinna, Thomas’ wife. Swift Services has its head office along Longpoint Road in Houston, Texas. It also has two branches in Houston and others in Baytown, Texas. Despite the company having most of its offices in Texas, it is licensed in 48 states (Swift Services, n.d.). Swift Services has approximately 40 employees who work as per the company’s organizational structure and culture.
1.2 Project Introduction
The freight company provides rental and equipment sale services (Swift Services, n.d.). Rental services are rendered within Houston, Texas. This includes fuel trucks, tractors, bucket trucks, vans, dump trucks, service trucks, pickup trucks, yard mules, specialized vehicles and equipment, water trucks, trailers, and skate beds (Swift Services, n.d.). Equipment sales include pioneer truck houses and cabs. Swift Services also provides busing services for companies as well as schools within Houston. The busing services are categorized as turnaround busing, tours, project transportation, shuttle services, dedicated contract services, and charters. Swift Services has a commendable fleet of yard mule tractors that are rented for gas and oil projects. Consequently, the company receives a good income. Also, its busing services are largely used by Fortune 500 companies, hence receiving a high flow of income. Some of Swift Services’ competitors are Yard Mule Specialists and AFC Houston. Yard Mule Specialists provide services like those provided by Swift Services through their fleet of yard mules (Yard Mule Specialists Texas, n.d.). However, Swift Services focuses on the Texas market, while Yard Mule Specialists serve four more states: Arkansas, Louisiana, New Mexico, and Oklahoma. Serving a bigger market is advantageous for Yard Mule Specialists because the company could receive more income and customer sensitization. AFC Houston, like Swift Services, provides busing services in Houston, Texas (AFC Houston, 2018). However, AFC Houston, unlike Swift Services, only focuses on busing services.
1.3 Problem Identification
1.3.1 Problem Context and Background
The problem at Swift Services is that customers have to call in or send emails to check on their parcels. A customer service representative then makes calls to other departments of Swift Services to inquire about delivery progress. This process is tedious and time-consuming, hence, prone to inaccuracy. Tracking systems that are not real-time have a high risk of parcel misplacement (Goll & Bolte, 2020). For example, Swift Services has several offices where parcels could be sent to three locations before reaching their destination. If one of the three offices in Texas captures a parcel’s details inaccurately, the parcel would be difficult to trace. It would be more difficult to trace a parcel if it was transported across states, resulting in delayed delivery. Swift Services is licensed for freight in 48 states (Swift Services, n.d.). The customer expected the parcel would be inconvenient and would provide a bad review. If more than one customer leaves a bad review on parcel delivery, new and existing customers would be hesitant to use the freight services. Consequently, Swift Services would lose income.
The inefficiencies observed in Swift Services when transporting and delivering parcels cause a negative impact on both customers and the staff. Customers are inconvenienced while the staff is exhausted. The performance of the company is negatively affected when the staff is constantly exhausted, resulting in staff underperformance. This necessitates the development and customization of a tracking system for Swift Services Company.
A parcel tracking system enables a company and its customers to trace the parcel as it is transported to its destination (Kunnari, 2018). This improves communication and facilitates parcel management. Also, with a tracking system, a company could handle more parcels within a shorter time efficiently. This would result in an increase in the company’s income. Customer satisfaction is achieved; hence, it maintains current customers while attracting new ones. Staff in the company would have less tedious tasks and enough time to offer efficient services to customers (Kunnari, 2018).
1.3.2 Problem Statement
Parcels transported by Swift Services are difficult to track, resulting in inefficient services. Customers are inconvenienced while the staff is exhausted. Consequently, the company’s performance is inadequate, and the company could lose income.
2. Solution Identification
2.1 Solution Framework
To resolve the inefficiency in freight services at Swift Services Company, a tracking system should be implemented. This would include a portal where customers would log in and use their receipt number to track their parcel. The tracking process would be made possible using intelligent port technologies. Such technologies include Radio Frequency ID, Machine to Machines, sensors, magnetic identification cards, and Wireless Sensor Networks (M’handa et al., 2019). In Radio Frequency ID, a tracker would be attached to the parcel while a reader would be in the system. The tracker would rely on location information to the system through the reader for the customer to read. In Machine to Machine, machines would be used to send information. For example, a machine in the field would send information to the central machine. Sensors would be used to detect environmental changes and send electrical signals to the tracking system. For Magnetic identification cards, parcels would contain a magnetic band at the back. The parcels would be swiped at specific transportation points for the information to be captured in the tracking system. Wireless Sensor Network would use distributed processing to collect parcel information and update the tracking system.
All the solutions provided would be used to update the tracking system. However, not all the solutions provided are real-time. Real-time solutions include Radio Frequency ID, sensors, and Wireless Sensor Network (M’handa et al., 2019). Based on cost and efficiency, the Sensor technology would be ideal for Swift Services Technology.
2.2 Hypothesis Statement
Implementing a tracking system for Swift Services would enhance the company’s performance, hence satisfying customers and increasing income.
2.3 Research Questions
How will a tracking system help in correcting reports’ inconsistencies and errors in the Swift Services Company’s system?
2.4 Related Works
In 2019, the Roll-on/roll-off (RoRo) company was advised to implement a real-time tracking system (M’handa et al., 2019). This would replace its periodically updated tracking system. RoRo was experiencing problems similar to those that are currently being experienced by Swift Services Company. The two companies used staff to manually update the tracking system. However, RoRo transports cargo on the sea while Swift Services does not (M’handa et al., 2019). Real-time tracking would improve efficiency at RoRo because, previously, cargo details would only be updated at the port. This made it difficult to estimate cargo traffic and offloading, especially when ships arrived simultaneously. But with real-time tracking, the staff at the port would identify in advance the ship that would arrive first and its contents (M’handa et al., 2019). Making the process of offloading efficient.
A study conducted for a Swedish retailer that was not using real-time parcel tracking also indicated similar problems to those of Swift Services Company (Goll & Bolte, 2020). For the retailer, goods would be recorded on two different systems. One within the company and another at the point of switching the goods with a third party. When capturing details on the second system, some goods would be left out, making the services inefficient. The goods could be misplaced or completely lost (Goll & Bolte, 2020). This problem would be solved by real-time tracking. At Swift Services Company, receiving parcels between two offices would result in the same problem the Swedish retailer was experiencing (Swift Services, n.d.). Therefore, the same solution offered to the Swedish retailer would be suitable for Swift Services Company.
Research on the globalization of supply chain management indicates why real-time tracking is important (Kunnari, 2018). Logistics companies in different countries partner to ensure that customers receive their goods with convenience. Therefore, when using racking systems that are updated periodically, updates would be made when handing goods to the next logistics company for delivery to a different country. Such an update would be prone to errors (Kunnari, 2018). This is because the process would be tedious and time-consuming. It would also be difficult to estimate which goods would arrive first when more than one truck was involved (Kunnari, 2018). This study is similar to that made at Swift Services, and the proposed solution would be similar, too.
3. Research Methodology
3.1 Research Matters
The research part of this project would facilitate information collection and solution modeling. This would involve staff at the Swift Services Company and customers or staff who could pose as customers for system simulation purposes. An adequately conducted research methodology is important in arriving at an accurate solution. For example, some experiments conducted by Yoo et al. (2018) for real-time location tracking for healthcare proved important in simulating the proposed system. The research part of the real-time location tracking for healthcare included asking medical professionals some questions about their current system. Nurses mentioned they were responsible for some hospital equipment during their shifts. However, it was difficult to transfer the responsibility of the medical equipment to a nurse on the next shift without a real-time location tracking system. The study by Yoo et al. (2018) aimed to reduce administration errors that would reduce the time used to hand over medical equipment at the end of a shift. This research focuses on solving parcel transfer errors that lead to delays in parcel delivery, rendering the company inefficient. Real-time tracking systems have been proven to eradicate errors and improve a company’s performance, making it a good recommendation for Swift Services (Goll & Bolte, 2020; Kunnari, 2018; M’handa et al., 2019; Yoo et al., 2018).
3.2 Experiment Design
3.2.1 Experiment Requirements
To conduct an experiment on the proposed solution, 480 parcels would be tagged with a Radio Frequency Identification tag and sent out to the various destinations. This means that all other parcels in transit would be on the current system, manually updating the parcel’s location on the system. Swift Service Company operates in 48 states; therefore, parcels would be distributed equally for delivery: 10 parcels per state. The experiment will be conducted in three weeks to ensure that data is adequately collected. Feedback would be collected from customers who received parcels tracked in real-time. The staff at Swift Services Company, who were involved in the process of receiving the parcel from the sender and delivering the parcels to the receiver, would also provide feedback. Observations made from the manually updated system and real-time tracking system would then be recorded. This would include having parcels that contain a Radio Frequency Identification tag transported by a different truck from parcels whose location would be manually updated.
For data collection, clients who send and receive parcels on the real time tracking system would be requested to fill a simple questionnaire. Staff at Swift Service Company involved in both the current system and the proposed system would also fill in questionnaires. This would be used to identify how satisfied the customers are with the services obtained on the proposed system compared to the current system. The efficiency of the proposed system would be evaluated based on customer feedback. Staff operating the proposed system would answer questions on the questionnaire to identify how easy it was to offer services on the proposed system. Both customers and staff would be requested to suggest improvements to the proposed system. Observation methods would be used to check system efficiency by noting how long it took to deliver a parcel and how easy it was for staff and customers to use the system. The results of the experiments would then be published for further reference.
3.2.2 Experiment Procedures
Unified Modeling Language (UML) would be used to present the experiment procedures for the proposed real time tracking system. UML diagrams are standard in designing systems because they create visual models that are easily understood (Koç et al., 2020). These models are essential during the system development process to ensure that all system requirements are captured. UML diagrams can continually be revised until an acceptable diagram is arrived at (Ciccozzi et al., 2019). Below is a UML diagram for the proposed real-time tracking system.
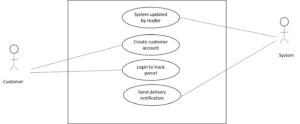
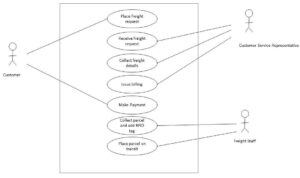
Figure 1: UML Diagram for the proposed real-time tracking system
The proposed system would have three actors: the customer, customer service representative, freight staff, and the utilized system. A customer would be required to request freight services. Then, a customer service representative would respond to the customer and note the flight details. Based on the details provided, the customer would be billed. After payment, a freight staff would collect the parcel. A Radio Frequency Identification tag would be attached to the parcel. This would automatically be updated in the system through the reader. From that point onwards, the customer could log in to the portal and track the movement of the parcel until its destination. This means that a customer can create an account and use the parcel receipt number to track his parcel. Upon delivery of the parcel, the system would send a delivery notification to the client. This is optional, as the customer must specify whether or not to receive the notification. The UML model could be remodeled when necessary to capture all the requirements of the proposed system. This would be based on system user feedback.
4. Project Plan
4.1 Project Plan for Data Collection & Analysis
Project planning is done to ensure that all tasks in a project are completed successfully. To perform data collection for the tracking system in the Swift Service Company, primary data collection would be conducted. Primary data collection methods are used to obtain data from scratch (Kabir, 2016). The primary data collection methods for the project would include questionnaires, observation, and case studies. Customers and staff at Swift Services will be asked to answer simple questionnaires. This would be useful in ensuring that correct data is used for data analysis. Observation would be conducted by checking how the tracking system works. For example, how do the users interact with the system and the output? Case study analysis would compare similar studies that have been conducted before and identify useful information for the project. The data analysis tasks would include converting the data collected into system requirements. Thereafter, the requirements would be implemented in system design.
A Gantt chart is used to list and schedule project resources to ensure that a project is completed within the estimated duration (Evdokimov et al., 2018). The Gantt chart in figure 2 below illustrates how tasks and human resources would be scheduled. Project duration is estimated at 34 days. The team would consist of five members; a project manager, a business analyst, an app designer, and two programmers. During system testing, three system users would be engaged. These would include both customers and staff.
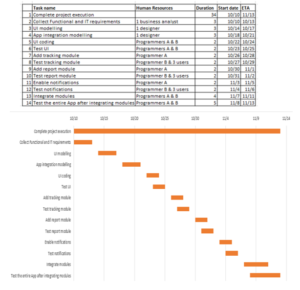
Figure 2: Gantt Chart for the proposed tracking system at Swift Services Company
The Gantt chart would enable the project manager to check on the project’s progress and identify any lagging. System requirements would be modeled by the application designer after data collection and analysis are completed. Thereafter, two programmers would commence the application development. Each module would be developed by programmers, and one programmer would begin testing the module with system users. Testing for a module is planned to start a day after its development has started and will continue until completion. After all the modules are completed, they shall be integrated and tested. To ensure that the whole system works as expected.
The estimated cost for each task would be calculated using Function Point Analysis (FPA). FPA uses a formula; FP = UFP * VAF, to estimate the cost of each task in a software project (HeydarNoori, 2018). UFP is Unadjusted Function Point, and VAF is Value Adjusted Factor (HeydarNoori, 2018). UFP consists of External Interface File and Internal Logical File. VAF is rate 0 – 5 based on system characteristics (HeydarNoori, 2018).
| Function Type | Function Complexity | Complexity
Totals |
Function
Type Totals |
||
| Internal Logical File | 20 | Low | X7 | 140 | |
| 30 | Average | X10 | 300 | ||
| 50 | High | X15 | 750 | ||
| 1190 | |||||
| External Interface File | 20 | Low | X5 | 100 | |
| 30 | Average | X7 | 210 | ||
| 50 | High | X10 | 500 | ||
| 810 | |||||
| External Input | 20 | Low | X3 | 60 | |
| 30 | Average | X4 | 120 | ||
| 50 | High | X6 | 300 | ||
| 480 | |||||
| External Output | 20 | Low | X4 | 80 | |
| 30 | Average | X5 | 150 | ||
| 50 | High | X7 | 350 | ||
| 580 | |||||
| External Inquiry | 20 | Low | X3 | 60 | |
| 30 | Average | X4 | 120 | ||
| 50 | High | X6 | 300 | ||
| 480 | |||||
| Total UPF count | 3540 |
Table 1: UFP for the proposed tracking system at Swift Services Company
| General system characteristics | Degree of influence(0-5) |
| Distributed data processing | 5 |
| Reusability | 5 |
| Installation ease | 4 |
| Operational ease | 4 |
| End-user efficiency | 5 |
| Performance | 5 |
| Data communications | 5 |
| The total degree of influence | 33 |
| Value Adjustment Factor (TDI*0.01)+0.65 | 0.98 |
Table 2: VAF for the proposed tracking system at Swift Services Company
FPA calculation for the proposed tracking system would be as follows;
FPA = UFP * VAF
= 3540 * 0.98
=3469.2
4.2 Risk and Cost-Benefit Analysis
Risk analysis is conducted to ensure that all risks are eliminated, avoided, or mitigated (Dumbravă & Iacob, 2013). Therefore, risk analysis was performed for the proposed tracking system. This began by listing all risk factors that were considered as major, then mapping them on a likelihood and impact matrix.
| Risk | Code | |
| 1 | Scope variations | A |
| 2 | Stakeholder expectations | B |
| 3 | Poor code quality | C |
| 4 | Poor project management | D |
| 5 | Budget changes | E |
| 6 | Inadequate risk management | F |
| 7 | Inaccurate estimation | G |
| 8 | Low stakeholder engagement | H |
| 9 | Inadequate skilled team | I |
Table 3: Risks for the proposed tracking system at Swift Services Company
| LIKELIHOOD | Very high | A | ||||
| High | D, J | |||||
| Medium | B | C | F | |||
| Low | H | I, E | ||||
| Very low | ||||||
| Very low | Low | Medium | High | Very high | ||
| IMPACT | ||||||
Table 4: Likelihood and impact matrix for the proposed tracking system at Swift Services Company
Cost-benefit analysis checks the financial viability of a project by comparing different ways that a project can be implemented based on cost (Hemakumara, 2017). Therefore, it is important to have a cost benefit analysis for all projects, including for the proposed tracking system.
| Stages | Cost
|
Cost in USD | Benefit | Benefit in USD |
| 1 | Development | 40,000 | Tracking system | |
| 2 | Operation | 5000 | Improved freight service, more transactions | 15,000,000 |
| 3 | Maintenance | 5000 | ||
| Total | 50,000 | 15,000,000 |
In 2019, Swift Services made 13,000,000 USD. With the tracking system, the company can increase revenue to 15,000,000 USD (Swift Service, n.d.). Development cost is one-off while operation and maintenance costs are low and yearly. Therefore, the total cost of 50,000 USD is viable compared to the revenue expected.
5. Conclusion and Future Works
5.1 Conclusion
5.2 Limitations
5.3 Future Works
Abstract and Keywords
TBD
References
AFC Houston. (2018, June 19). About us. Retrieved from https://afchouston.com/about-us/
Ciccozzi, F., Malavolta, I., & Selic, B. (2019). Execution of UML models: a systematic review of research and practice. Software & Systems Modeling volume, 18(2019), 2313–2360. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10270-018-0675-4
Dumbravă, V., & Iacob, V. S. (2013). Using Probability – Impact Matrix in Analysis and Risk Assessment Projects. Journal of Knowledge Management, Economics and Information Technology, 76-96. Retrieved from http://www.scientificpapers.org/wp-content/files/07_Dumbrava_Iacob-USING_PROBABILITY__IMPACT_MATRIX_IN__ANALYSIS_AND_RISK_ASSESSMENT_PROJECTS.pdf
Evdokimov, I. V., Tsarev, R. Y., Yamskikh, T. N., & Pupkov, A. N. (2018). Using PERT and Gantt charts for planning software projects on the basis of distributed digital ecosystems. Journal of Physics Conference Series, 1074(2018), 1-7. Retrieved from https://www.researchgate.net/publication/328177467_Using_PERT_and_Gantt_charts_for_planning_software_projects_on_the_basis_of_distributed_digital_ecosystems
Goll, D. C., & Bolte, N. O. (2020). Potential analysis of track-and-trace systems in the outbound logistics of a Swedish retailer (Master’s thesis, Jönköping University, Jönköping, Sweden). Retrieved from http://www.diva-portal.org/smash/get/diva2:1436505/FULLTEXT01.pdf
Hemakumara, G. (2017). COST-BENEFIT ANALYSIS OF PROPOSED GODAGAMA DEVELOPMENT NODE UNDER THE GREATER MATARA DEVELOPMENT PLANNING PROGRAM. International Research Journal of Management and Commerce, 4(9), 9-19. Retrieved from https://www.researchgate.net/publication/320125260_COST-BENEFIT_ANALYSIS_OF_PROPOSED_GODAGAMA_DEVELOPMENT_NODE_UNDER_THE_GREATER_MATARA_DEVELOPMENT_PLANNING_PROGRAM
HeydarNoori, A. (2018). Function Point Analysis. Retrieved from https://cs.uwaterloo.ca/~apidduck/CS846/Seminars/abbas.pdf
Kabir, S. M. (2016). Chapter: 9 METHODS OF DATA COLLECTION. In Basic Guidelines for Research: An Introductory Approach for All Disciplines (pp. 201-275). Retrieved from https://www.researchgate.net/publication/325846997_METHODS_OF_DATA_COLLECTION
Koç, H., Erdoğan, A. M., Barjakly, Y., & Peker, S. (2020, December). UML Diagrams in Software Engineering Research: A Systematic Literature Review [Paper presentation]. 7th International Management Information Systems Conference. https://www.mdpi.com/2504-3900/74/1/13/pdf
Kunnari, J. (2018). Track & Trace Solution for Road Cargo in Paper Industry (Master’s thesis, Tampere University of Technology, Finland). Retrieved from https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/250162232.pdf
M’handa, M. A., Boulmakoulb, A., Badira, H., & Lbath, A. (2019). A scalable real-time tracking and monitoring architecture for logistics and transport in RoRo terminals. Procedia Computer Science, 151(2019), 218–225. Retrieved from https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1877050919304946
Swift Services. (n.d.). Houston’s top commercial trucking & fleet management service. Retrieved from https://www.swiftservices.net/ABOUT-US
Yard Mule Specialists Texas. (n.d.). Terminal tractor | Yard mule specialists | United States. Retrieved from https://www.ymstexas.com/
Yoo, S., Kim, S., Kim, E., Jung, E., Lee, K. H., & Hwang, H. (2018). Real-time location system-based asset tracking in the healthcare field: lessons learned from a feasibility study. BMC Medical Informatics and Decision Making, 18(80). https://bmcmedinformdecismak.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12911-018-0656-0
ORDER A PLAGIARISM-FREE PAPER HERE
We’ll write everything from scratch
Question 
Tracking System Solution For Swift Service Company
After the experiments have been designed and developed, the next step should be executing the experiments to collect the data, and then to conduct data analysis. However, restricted by the time, for this class, we will only develop a project plan for the tasks of executing experiments to collect data, and to analyze data in order to answer the research questions and validate the solution.
For this assignment, you will continue your work on the project with the development of a project plan for data collection and analysis. You will first develop a list of concrete tasks for data collection and analysis. Then, you need to develop the project timeline and identify the required human resources, as well as the estimated costs that are necessary for the execution of each task. You will also examine the risks in the project and determine how to mitigate those risks. Finally, you will perform a cost-benefit analysis of the project and its value to the company.
The following are the project deliverables:
Update the Computer Science Problem-Solving Research Project Report document title page with a new date and project name.
Update the previously completed sections based on instructor feedback.
New Content for Week 4:
4. Project Plan
4.1 Project Plan for Data Collection & Analysis
Tasks
Develop a list of Data Collection and Data Analysis tasks.
Time Line and Human Resource
Develop a project timeline for each task.
Assign the human resources to each task.
Ensure that all required tasks are identified in the timeline and that each task has dedicated human resources so that the project can be completed within the available time frame.
Estimated cost
Provide an estimated cost for each task.
4.2 Risk and Cost-Benefit Analysis
Provide a risk analysis for the project that identifies major risks and mitigation strategies.
Provide the Cost-Benefit analysis for the project.