Fiscal Policy Simulation
Simulation Analysis
The simulation results show a progressive reduction of the debt level due to the application of different fiscal policies. One of the successful debt reduction policies in the simulation scenario was the institution of spending cuts. Also, raising taxes to fund government expenditures reduces government debt in the long run. Overall, spending cuts are crucial to lowering a country’s national debt burden.
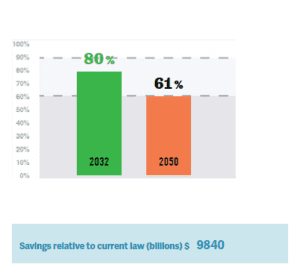
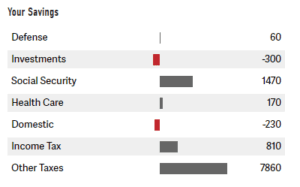
Impact of High National Debt on Economic Growth
There is an inverse relationship between national debt and economic growth. As the national debt increases, the prospects of a country attaining economic growth drop. Countries that borrow to fund massive infrastructural projects get the worst outcomes.
Firstly, as a country’s loans increase, the chances of defaulting also go up. As a result, the Treasury increases yields for newly issued securities to attract new investors (Muthari, 2015). High payoffs mean that the interest rates on loans are high. The government has limited finances for other government development projects and services. As the debt level burgeons, the government will have less to spend on other economic improvement projects.
Also, as the national debt level increases, investors in the securities exchange market raise the risk level. As a result, companies respond by raising yields due to investors (Muthari, 2015). These companies transfer the costs to the final consumers by raising the price of their goods and services. Therefore, a high national debt triggers inflation, which hinders economic growth.
The Crowding-Out Effect
The crowding-out effect refers to a situation where interest rates are so high that the private sector is discouraged from borrowing to fund capital investment projects. Crowding out occurs when a government adopts an expansionary fiscal policy (Mankiw, 2016). The cost of lending goes up as the government borrows aggressively. A high-interest rate massively discourages the investment decision of the private sector.
As the cost of borrowing goes up, it significantly limits the private sector’s access to funds. Even the initial investments already in place are crowded out due to a lack of financing (Mankiw, 2016). The crowding-out effect occurs when the government’s increased spending is funded through borrowing.
References
Muthari, L. K. (2015). The effect of national debt on economic growth in Kenya (Doctoral dissertation).
N Gregory Mankiw. (2016). Principles of microeconomics. Cengage Learning.
ORDER A PLAGIARISM-FREE PAPER HERE
We’ll write everything from scratch
Question 
Fiscal policies are used by the government to stabilize the economy. During the 2020 emergency caused by the coronavirus pandemic, the U.S. government approved a stimulus package that increased the U.S. debt.

Fiscal Policy Simulation
For this discussion, first play the simulation The Debt Fixer (from the Committee for a Responsible Federal Budget), in which you make fiscal policy decisions in an attempt to reduce the U.S. debt. You can play the simulation as many times as you like.
In your initial post, include an image of your simulation report. (See Module Six Simulation Discussion Screenshot Instructions PDF.) Then address the following:
- Share your experience in the simulation. What strategies did you pursue? Were you successful in reducing the debt?
- In your opinion, is a high national debt a problem for future economic growth? What is the ideal debt-to-GDP ratio? Research academic sources or refer to the information available through the simulation to support your opinion.
- Government spending increases national debt and can cause a crowding-out effect. Explain what the crowding-out effect is and why it’s considered a negative effect of increased government spending. Use information from the textbook to support your analysis.
In your responses, comment on at least two posts from your peers by comparing and contrasting your experiences and opinions. Share current news articles or references from the textbook that support your decisions in the simulation and your claims related to the national debt.