CommunicationStrategy for Adaptive Leadership Toolkit Implementation
Organizational Improvement: Business Problems
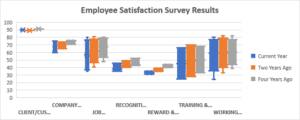
The current problems that the organization is facing revolve around specific focus areas. These areas include company & strategy, job satisfaction, recognition and praise, reward and recognition, training & development, and working conditions. According to the employees, their leaders do not acknowledge their efforts. This lack of recognition is present despite the employees’ abilities to fulfill their objectives. At other times, the employees are not aware of the goals and objectives they should work towards. Due to lack of training and development, the employees feel that their skills and abilities are not utilized. In addition, the presence of unethical practices and unjust leadership erodes any trust that employees may have in their leaders. The lack of moral support for employees as they go through personal issues also comes across as a problem.
Role of the Personal Development Plan
The personal development plan was created to function as a guide for individual leaders. It highlights the weaknesses and strengths of everyone. It also guides the development of SMART goals. Its presence evokes concern and commitment from the leaders, who are further analyzed using an employee survey, highlighting specific issues.
Role of the Adaptive Leadership Toolkit
The adaptive leadership toolkit is ideal for resolving these issues in several ways. First, it will address the training and development needs by requiring the supervisors to receive training on leadership through the supervisor toolkit. In addition, web-based or leader-led training will offer employees an opportunity to improve their skills. Secondly, the skills assessment will highlight the company’s training needs. Thirdly, the ethical tone messaging toolkit will sensitize the leaders and supervisors to incorporate ethical tones in their meetings and communications.
Leadership strengths
Based on the employee satisfaction survey, the main leadership strengths include clear goal definition, value for clients, necessary tools for work activities, fair and competitive compensation, job security, respect for employees’ diversity, work safety, and provision of support to employees as regards fulfillment of family obligations. Some of these strengths have inspired significant job satisfaction and created a positive perspective regarding the organization’s regard for clients.
In such an organization, providing a safe work environment, respect for workforce diversity, and competitive/fair job compensation shows that the entity is compliant. This implies that the company does not discriminate and utilizes the differences within the workforce to attain a competitive advantage, which facilitates competition with other players. In addition, the presence of quality goals and the necessary working resources, as well as tools, empowers employees to perform their roles effectively. Most importantly, providing clients with value for their money allows the organization to create a loyal market share that constantly refers to other people leading to increased revenue. Finally, fair and competitive compensation reduces the likelihood of a high turnover rate that would have dire effects on the quality of products and services and increase recruitment costs.
The analysis highlights areas that the leaders are effective at. These areas, which are strengthened, inform the HR professionals about areas that do not need to be included in the leadership toolkit. This information guides the development of the toolkit to ensure it addresses the weaknesses first. The toolkit can also build on these strengths to develop the faults. It also guides the allocation of financial and human resources.
Leadership weaknesses
The main points of weakness include the lack of a shared vision that should motivate employees to believe in and work towards a common goal with higher commitment. The lack of concern for its employees demonstrates neglect. Lack of job satisfaction is apparent as the employees feel unutilized. They also feel that their skills and abilities are not utilized efficiently while training and development opportunities continue lacking. Furthermore, failure to acknowledge, recognize, and reward employees following the achievement of goals leads to discouragement. The lack of ethical and just leadership practices places immense doubt in employees regarding the company’s ethical position. Lack of trust and inclusive decision-making makes employees feel less valuable to the entity.
To improve the current weaknesses, the organization’s leadership should enhance its ability to inspire a shared vision, model the way, and challenge the process. Improving these abilities involves having leaders who can set examples using their decisions and actions. They should also inspire the employees to understand and believe in the company’s vision and mission (Martin, McCormack, & Fitzsimons, 2014). Most importantly, creating a culture of innovation is essential in encouraging employees to devise new strategies for fulfilling objectives and goals.
Based on the analysis of the results, the adaptive leadership toolkit will be instrumental in resolving the current issues. As the results reveal, communication, poor ethics, lack of inclusivity, poor team management, and lack of recognition or training top the list of the leader’s weaknesses. This means that the adaptive toolkit must address these behaviors by seeking to improve or impart knowledge and skills to the leaders. The ethical tone messaging toolkit, the performance of skills assessment, and actual training and development are geared towards improving the identified weaknesses. The main gaps that guide the toolkit include corporate culture, motivation, and skills/knowledge.
A personal development plan
A personal development plan is strategic for self-improvement. The plan creates a clear idea of career-related aspirations. Through comprehension of various goals and objectives, an individual can begin the journey toward self-improvement. It also motivates the involved parties to steer towards the identified direction. In this case, a personal development plan contributes to the adaptive leadership toolkit implementation and the organization. Creating a personal development plan creates awareness of an individual’s weaknesses and strengths. With this information, an individual knows they can work on their shortcomings using the adaptive leadership toolkit. Therefore, the personal development plan sets the leaders’ mental state in a position of improvement, leading to the acceptance of the toolkit and commitment to the process. As a result, the organization’s management and leadership are more likely to go through the implementation process with a higher likelihood of success (Rolfe, 2021).
The organization is facing problems related to training and development, recognition, reward, working conditions, company and strategy, and job satisfaction. these problems arise from the leaders’ behaviors. Their lack of knowledge regarding the impact that some of their behaviors have on the organization and the employees is the root of the problem. The awareness that results from the personal development plan brings to the leaders’ attention their shortcomings and negative elements. The opportunity to address these weaknesses is aligned with the organization’s desire to improve the leaders’ behaviors using the adaptive leadership toolkit.
The personal development plan and SMART goal setting are instrumental in developing the individuals’ leadership styles within the organization. As stated earlier, SMART goals offer guidance, while the personal development plan charts a clear direction toward the destination. The need to improve leadership styles calls for commitment from leaders. The leaders need to be in touch with their weaknesses and aware of their strengths. This information highlights areas that they excel in and those that they must improve. The SMART goals come in handy when identifying the elements that need to be fulfilled to improve the current weaknesses. With well-articulated SMART goals, it is easy for leaders to improve on certain aspects that are important in achieving effective and efficient leadership (First Nations Development Institute, 2018).
Adaptive Leadership Toolkit
The adaptive leadership toolkit will benefit numerous stakeholders. First, the leaders will reap direct benefits from the toolkit as they undergo training and skills assessment. This toolkit benefits leaders directly because it is created for their primary use. It is intended to help them improve their managerial, communication, and team management skills. It is a product of the current shortcomings that influence the workforce negatively in the organization.
Secondly, the trainers will use the toolkit during the process of implementation. The organization plans to outsource external parties to conduct the training and skills assessment and a survey. These outsourced trainers will use the toolkit as they actualize it through the training sessions. Their interactions with the management and the leaders during the toolkit’s actualization will help determine if the strategy is ideal for achieving the set goals.
Thirdly, the employees will use the toolkit indirectly. Employees’ feedback of leaders’ performance at the organization has resulted in the creation of the toolkit. Therefore, implementing the toolkit in improving the leaders’ skills and abilities will benefit employees as the work conditions improve. Other elements that are expected to improve include work ethics, support from the leaders, reward systems, and motivation programs. In addition, their constant feedback on the leaders’ performance will lead to the improvement of the toolkit.
Finally, the clients will use the toolkit in the same manner as employees. When employees are not satisfied or happy with their jobs, they are likely to perform poorly. This performance results in poor service delivery. The outcome may include loss of clients and lack of satisfaction. However, the process of improving leaders’ skills and abilities is expected to turn this around as employees put in more effort due to motivation. Clients are likely to receive better services and value for their money. Thus, they use or benefit from the program, albeit indirectly.
The adaptive leadership toolkit belongs to the organization’s human resource department. Following a survey that sought to establish the leadership elements of the entity, the HR team found out that the employees have a negative perception of their leaders. This information resulted in the creation of a toolkit that was designed to improve the current leadership. Therefore, the toolkit is an organization’s intellectual property that is created for use by leaders, employees, and trainers.
As such, the human resource department will be responsible for overseeing the entire process of implementation. The department will design the details that affect its implementation, outsource trainers and other specialists, kickstart feedback collection and analysis processes, and ensure that the implementation goes according to the plan. Management of the toolkit is essential because HR ensures that the set goals and milestones are achieved. This aspect is critical in assessing the company’s Return on Investment (ROI).
Leadership skills and behaviors that are included in the adaptive leadership toolkit
Communication is one of the leadership skills and behaviors that is included in the toolkit. Communication is an essential element for seamless leadership and interactions with employees. Leaders are expected to hear their employees’ concerns and show empathy by acting. Failure to utilize communication as a strategy for connecting with employees interferes with the leader’s ability to create an effective team. Communication creates the basis for encouraging employees, informing them about goals, and seeking the employees’ opinions. In addition, encouraging open communication from the staff members is essential in setting the various goals and objectives as well as assessing these. Employees tend to feel free to provide suggestions as well as make complaints in the workspace. Such inclusivity is essential for employees to feel valued and heard by the entity.
Ethical practices and transparency
According to the survey, employees believe that the leaders do not provide ethical leadership. This interferes with the employees’ perception of the organization’s values and their application by the leaders. Ethical leadership and transparency are essential in encouraging similar behaviors from the staff members. Once leaders adopt these behaviors, they are likely to inspire similar tendencies through a common vision. Employees are motivated when they see just and ethical leadership leading to the development of trust in the leaders. The absence of such leadership tends to create distrust and a lack of confidence in the leaders (Haque, Haque, & Islam, 2014). These are clearly lacking in the organization leading to a drop in the current state of working conditions.
Team management
Management of the teams is critical for optimum work performance. The workforce is not encouraged, motivated, appreciated, innovative, trained, or recognized in its current state. These aspects have led to a consistent drop in the reward and recognition as well as recognition and praise categories. Employees require constant motivation, encouragement, appreciation for their efforts, and training alongside recognition. The development of these behaviors among the leaders should improve their current managerial skills and change the workforce’s outlook regarding the leaders (Latham, 2004). It should also positively impact performance as employees demonstrate innovation and seek new ways to conduct their roles and responsibilities.
Empowerment
Empowering employees is an essential aspect of enabling them to complete their duties efficiently. Training and development are some of the strategies that can be used for empowerment. The other applicable approach is the provision of the necessary tools as well as setting goals and objectives while allowing employees to be innovative. The training imparts the skills that are necessary for the fulfillment of the job description. It also eliminates the feeling that their skills and abilities are not being utilized in their current positions. This opportunity to develop one’s career motivates staff to remain with an organization for longer. Therefore, it reduces the cost of recruitment, which could increase due to high turnover. Allowing employees to be innovative will enable them to demonstrate their creativity. Innovative strategies create chances to communicate and brainstorm. Employees begin to feel important to an organization’s activities because they become part of the solution. While innovation introduces risk, it also sets apart an organization because unique ways of completing roles and responsibilities are devised. The result is improved performance and increased revenue (Sharma & Shirsath, 2014). When leaders realize that they need to empower staff members in diverse ways, their responsibility to lead becomes easier.
Rollout and Implementation
| Toolkit element | Timeframe | Metrics | Deliverables |
| Ethical tone messaging toolkit
· Understand · Apply · Champion |
January-April 2022 | Nine percent increment in the first year | · Ethical leadership
· Ethical corporate culture · Clear organizational values |
| Skills assessment
· Skills inventory · Communicate intentions · Data collection · Data analysis |
May-July 2022 | Seven percent increment in the first year
Likert scale (1-5) |
· Inventory of the required workforce’s skills for various positions
|
| Training and development
· Assess training needs · Set training objectives · Create an action plan · Implement training initiatives · Evaluate and revise |
August-December 2022 | Ten percent increment in the first year | · Training needs analysis
· Clear objectives for training · Training program · Actual training sessions · Training materials and content
|
Based on the table above, the process of improving leadership skills and behaviors will take at least twelve months in 2022. This timeframe is not rigid and allows for extensions as the need arises. Activities such as training and development will be recurrent to address certain skill gaps. Thus, the activity will be conducted again to ensure that a learning culture is established and maintained. The process of training leaders and supervisors first is critical because these individuals’ behaviors set the pace for the employees. Therefore, training will empower supervisors and other managers to understand the organization’s objectives, vision, and mission. This understanding will highlight their assumptions and lead to learning as well as a change in behaviors. Leaders will also be sensitized to behaviors that demoralize the workforce and enable them to transfer their knowledge to staff members.
Metrics and deliverables
The entire program will be measured based on scores from previous years. The ethical tone messaging toolkit will be expected to increase the score by 9 percent during the first year. This will be determined by employees’ perception of leaders’ ethics, integrity, honesty, and trust in their abilities. The skills assessment will be expected to lead to a 7 percent increment in the company’s performance. This means that the employees’ skills will be expected to improve. In addition, a Likert scale that provides a measure of 1 to 5 will be used to assess the leaders’ proficiency in certain skills. One will refer to developing, while five will indicate mastery. The training and development section will be expected to result in a 10 percent increment during the first year. The primary abilities that are expected to improve significantly include team management skills, efficient communication, and time management skills. Surveys will be used to ascertain the employees’ perceptions of their leaders to track the progress of the toolkit’s elements. Besides a survey, the progress of the objectives will be monitored at the end of each program within the toolkit to identify any loopholes. Any unmet objectives will guide further action to ensure the goals are met completely. The collection of feedback will be important because the participants will provide their opinions on the entire process and criticize it, leading to improvement. Open communication will be critical in enabling the feedback collection process.
Methods for communicating
To communicate to leaders about the toolkit, various platforms will be used—meetings with leaders about the current survey and the employees’ opinions regarding the company’s management. The leaders will be allowed to air their opinions regarding the survey’s results and provide propositions on their perception regarding a leadership toolkit. During this meeting, the leaders will be informed about the benefits they will reap from the entire program. Since employees will also benefit from the program, they will be convened to inform them about the survey’s results and the action plan that will be taken in the future to change the situation. The employees’ and leaders’ opinions will be invited to improve the toolkit from the beginning.
Feedback and communication
Feedback will be provided using different platforms. First, the leaders and employees will be allowed to approach the executive team and share their ideas. Face-to-face communication through the open-door policy will be encouraged. Secondly, leaders in the training sessions will be allowed to approach the trainers and share their opinions about the processes, materials, content, and techniques. In addition, question and answer sessions will be held after sessions to understand if the leaders are benefitting or relate to the content. Thirdly, the leaders will be allowed to provide written feedback at the end of the program’s elements, especially if they want to remain anonymous. This information should highlight issues that have been addressed, issues that need better and more advanced content, areas that trainers could improve on, such as materials and techniques, and other elements that influence the toolkit’s effectiveness.
Fourthly, the survey will provide a tool for collecting the employees’ feedback after the leaders have completed their training. The survey is important because it will highlight leaders’ improvements in their managerial skills and abilities. This information is dependable due to the honesty of employees’ feedback and their direct interaction with leaders. It will form the basis for future training sessions to ensure the consistent improvement of leaders. Finally, each department will provide questionnaires to employees regarding the whole exercise periodically. These questionnaires will be open-ended and shall assess specific elements of the toolkit. They will allow employees and leaders to explain their responses, thus providing meaningful feedback.
To communicate this information to all members of the organization, meetings will be convened. Regular meetings that are intended to discuss the toolkit and its improvements will be the primary platform for communication. These meetings are ideal because they will allow discussions regarding these improvements to occur. In addition, the process of delivering the information face to face will highlight the nonverbal cues that employees may not vocalize. This provides an opportunity to address all these elements, ensuring that employees are satisfied.
Meetings at the departmental levels will be instrumental because the executive team and trainers will manage employees in small groups. Furthermore, any improvements that are specific to each department will be communicated to the relevant groups leading to meaningful discussions and quality feedback. In addition, memorandums will be written to communicate rapid changes that affect all departments. These memorandums will be listed on each department’s notice boards to ensure that all employees are well-informed. They will also be used to follow up the meetings’ discussions and function as reminders for employees about various meetings’ conclusions.
References
First Nations Development Institute. (2018). Successful Evaluation: Creating SMART Goals & Objectives. Retrieved from https://www.firstnations.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/12/EvaluationTips_SMARTGoalsObjectives.pdf
Haque, M. F., Haque, M. A., & Islam, S. (2014). Motivational Theories – A Critical Analysis. ASA University Review, 8(1), 61-68.
Latham, G. P. (2004). The motivational benefits of goal-setting. The Academy of Management Executive, 18(4), 126.
Martin, J., McCormack, B., & Fitzsimons, D. (2014). The importance of inspiring a shared vision. International Practice Development Journal, 4(2).
Rolfe, A. (2021). Five benefits of personal development.
Sharma, V., & Shirsath, M. (2014). Training –A motivational tool. IOSR Journal of Business and Management, 16(3), 27-35.
ORDER A PLAGIARISM-FREE PAPER HERE
We’ll write everything from scratch
Question 

CommunicationStrategy for Adaptive Leadership Toolkit Implementation
In this project, you will demonstrate your mastery of the following competencies:
- Craft a communication strategy for internal and external audiences
- Leverage internal and external intelligence to inform decision-making
- Develop an adaptable leadership mindset and skillset
Scenario
You work as a director of leadership and learning for an organization that makes prosthetics. The organization has been in business since 1999 and employs over 350 people in its Tampa, Florida, headquarters and three plant locations across the Southwest. While the company is currently based in the United States, the organization is exploring ways to move into Canadian markets within the next three years. This year’s employee engagement survey results show that some leadership practices are rated lower while others are higher. The new chief human resources officer (CHRO) met with the team to discuss the general results. Everyone agrees that the company’s focus should be on specific leadership development areas perceived as strengths and those rated as areas for improvement, primarily regarding social intelligence, emotional intelligence, and the interpersonal skills of effective leaders.
To help this initiative, your manager, the vice president of leadership and learning, asked you to create an adaptive leadership toolkit that can be used throughout the organization. You conducted a personal leadership self-assessment to begin this work and turned this into a personal development plan. Then you shared this artifact with your manager. Your manager was impressed with the thoroughness of the personal development plan and saw value in incorporating it as an exemplar within the adaptive leadership toolkit for use by all people leaders in the organization. After receiving such positive feedback, you created the rest of the adaptive leadership toolkit.
Your manager has shared the adaptive leadership toolkit you created with the CHRO, and it was well-received. The CHRO wants to distribute this toolkit to all leaders—supervisors and above—and asks you to create a communication strategy that will help roll out and implement the adaptive leadership toolkit. For this project, you will make that communication strategy.
Directions
Overview: In this part of the communication strategy, you will summarize the business problems the organization is currently experiencing and provide an overview of trends from your analysis. You will also explain how a personal development plan and adaptive leadership toolkit can solve these challenges.
- Summarize the business problems the organization is currently facing and describe how the personal development plan and adaptive leadership toolkit will address them.
- Why was the personal development plan created?
- Why was the adaptive leadership toolkit developed?
- Summarize trends in leadership strengths observed in your employee satisfaction survey analysis and describe how they relate to the leadership skills and behaviors included in the adaptive leadership toolkit.
- In which areas did leadership score well?
- How did your analysis help inform skills and behaviors included in the adaptive leadership toolkit?
- Summarize trends in leadership weaknesses observed in your employee satisfaction survey analysis and describe how they relate to the leadership skills and behaviors included in the adaptive leadership toolkit.
- In which areas did leadership not score well?
- How did your analysis help inform skills and behaviors included in the adaptive leadership toolkit?
Personal Development Plan: In this part of the communication strategy, you will further describe the personal development plan. You will include how the personal development plan supports the adaptive leadership toolkit and its value once the entire toolkit is rolled out.
- Summarize the importance of including a personal development plan in the adaptive leadership toolkit and explain its value to the organization.
- How does the personal development plan support the adaptive leadership toolkit?
- How do the strategies within the personal development plan address the business problems the organization is currently facing?
- Explain how the personal development plan and SMART goal setting could help develop the leadership styles of the leaders within the organization.
Adaptive Leadership Toolkit: In this part of the communication strategy, you will describe the adaptive leadership toolkit in further detail. You will include how and who the adaptive leadership toolkit brings value to the organization.
- Describe how the adaptive leadership toolkit will be used and who will manage it. Your response should address the following:
- Who is the target audience for the adaptive leadership toolkit?
- Who are the owners of the adaptive leadership toolkit?
- Describe the specific leadership skills and behaviors that are included in the adaptive leadership toolkit and explain how developing these skills and behaviors will address the business problems the organization currently faces. Use trends from the employee satisfaction survey to support your response.
Rollout and Implementation: In this part of the communication strategy, you will provide more details about the rollout and implementation of the adaptive leadership toolkit throughout the organization.
- Provide a timeframe for the rollout and implementation of the adaptive leadership toolkit and justify how this strategy supports the organization’s goal of improving leadership skills and behaviors over the next two years.
- Describe the metrics and deliverables associated with the rollout and implementation of the adaptive leadership toolkit. Your response should address the following:
- How will the success of this rollout and implementation be measured?
- What are some important milestones to consider when tracking progress?
- Determine methods for communicating the relevance of the adaptive leadership toolkit to stakeholders within the organization. Your response should address the following:
- How should this be communicated to leadership to help gain buy-in?
- How should this be communicated to its intended users to help gain buy-in?
- Describe the feedback and communication strategy associated with continuous improvements to the adaptive leadership toolkit. Your response should address the following:
- How can employees provide feedback on any roadblocks, issues, or ideas for improvement?
- How will updates to the adaptive leadership toolkit be communicated from leadership down to employees?